04231
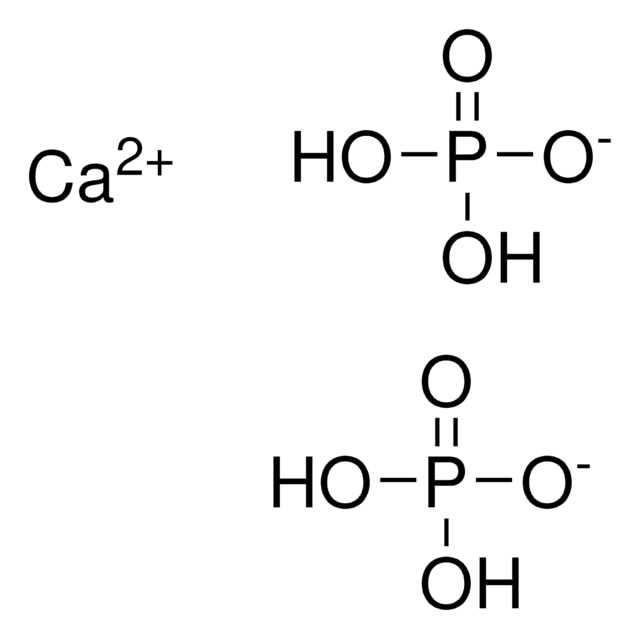
Calcium phosphate dibasic dihydrate
puriss., meets analytical specification of Ph. Eur., BP, USP, 98-102.5%
Synonym(s):
Calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
puriss.
Quality Level
Assay
98-102.5%
form
powder
quality
meets analytical specification of Ph. Eur., BP, USP
impurities
organic volatile impurities, complies
residual solvents, complies
≤0.003% heavy metals (as Pb)
≤0.1% insoluble in HCl
loss
24.5-26.5% loss on ignition, 800 °C
anion traces
carbonate (CO32-): in accordance
chloride (Cl-): ≤200 mg/kg
fluoride (F-): ≤50 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤3000 mg/kg
cation traces
As: ≤1 mg/kg
Ba:, in accordance (Ph Eur)
Ba:, in accordance (USP)
Fe: ≤300 mg/kg
SMILES string
O.O.[Ca++].OP([O-])([O-])=O
InChI
1S/Ca.H3O4P.2H2O/c;1-5(2,3)4;;/h;(H3,1,2,3,4);2*1H2/q+2;;;/p-2
InChI key
XAAHAAMILDNBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- Simultaneous Regulation of the Mechanical/Osteogenic Capacity of Brushite Calcium Phosphate Cement by Incorporating with Poly(ethylene glycol) Dicarboxylic Acid: This research investigates enhancing brushite calcium phosphate cements by adding poly(ethylene glycol) dicarboxylic acid to improve mechanical properties and osteogenic capabilities, applicable in bone regeneration and implant materials. (Gao et al., 2024).
- Biosurfactant-Assisted Cu Doping of Brushite Coatings: Explores the structural and biofunctional enhancements of brushite coatings through copper doping facilitated by biosurfactants, which could revolutionize surface treatments for biocompatible implants and devices. (Siva Prasad et al., 2024).
- Self-Healing Micro Arc Oxidation and Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate Double-Passivated Coating on Magnesium Membrane for Enhanced Bone Integration Repair: This study highlights the application of calcium phosphate dibasic dihydrate in developing protective coatings on magnesium-based implants, significantly advancing orthopedic and dental implant technologies. (Wu et al., 2024).
- Physiologically Engineered Porous Titanium/Brushite Scaffolds for Critical-Size Bone Defects: Details the design and fabrication of novel scaffolds for treating large bone defects, utilizing a combination of titanium and brushite, highlighting its potential in reconstructive surgery and regenerative medicine. (Abdulaziz et al., 2023).
- Mechanochemical Synthesis of Cerium Chlorapatite from a Mixture of Cerium Chloride Heptahydrate, Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate, and Calcium Hydroxide for Biomedical Application: Focuses on the innovative production of cerium chlorapatite using dicalcium phosphate dihydrate, showcasing its potential in biomedical engineering, especially in drug delivery and tissue engineering. (Otsuka et al., 2024).
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service