EC1
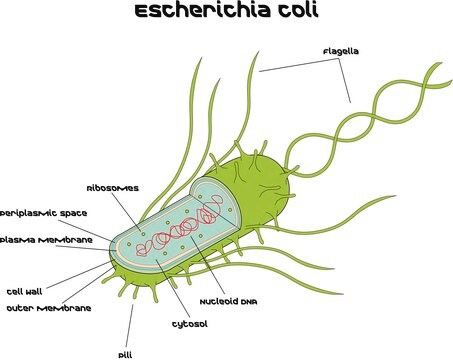
Escherichia coli
Strain K12, lyophilized cells
Synonym(s):
E. coli K-12
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
sterility
non-sterile (not processed or packaged aseptically)
form
lyophilized cells
suitability
not intended for starter culture
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Escherichia coli (E.coli) is a non-spore forming, Gram-negative, rod-shaped facultative anerobe, which is found in the human gastrointestinal tract. It belongs to the family of Enterobacteriaceae. E.coli is chemoorganotrophic and grows at 37°C. Pathogenic E.coli strains is associated with diarrhea, septicemia, meningitis and urinary tract infections. It inhibits the colonization of the gut by harmful bacteria. E.coli acts as an indicator of fecal contamination.
Other Notes
A mutant which is rich in alkaline phosphatase.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Joseph M Autry et al.
Analytical biochemistry, 610, 113965-113965 (2020-09-22)
We have analyzed protein expression and enzyme activity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-transporting ATPase (SERCA) in horse gluteal muscle. Horses exhibit a high incidence of recurrent exertional rhabdomyolysis, with myosolic Ca2+ proposed, but yet to be established, as the underlying
Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods.
Krumperman PH, et al.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 46(1), 165-170 (1983)
Min-Hui Zhao et al.
Biosensors & bioelectronics, 150, 111865-111865 (2019-11-20)
We develop a low-background electrochemical biosensor for one-step detection of uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) based on the host-guest interaction and iron-embedded nitrogen-rich carbon nanotube (Fe-N-C) that mimics enzyme-mediated electrocatalysis to achieve signal amplification. In this work, Fe-N-C is initially immobilized
D Semenova et al.
The Analyst, 145(3), 1014-1024 (2019-12-13)
The manufacturing of conventional enzymatic biosensors produced via a layer-by-layer (LbL) approach requires expensive instrumentation, and in most cases involves a complex, resource and time-consuming fabrication process. Moreover, LbL assemblies are prone to mechanical instability that leads to irreversible changes
Daria Semenova et al.
New biotechnology, 56, 27-37 (2019-11-11)
Design and development of scale-down approaches, such as microbioreactor (μBR) technologies with integrated sensors, are an adequate solution for rapid, high-throughput and cost-effective screening of valuable reactions and/or production strains, with considerably reduced use of reagents and generation of waste.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service