G6142
Glycerokinase from Cellulomonas sp.
lyophilized powder, 25-75 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
glpK, ATP:glycerol 3-phosphotransferase, Glycerol Kinase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(7)
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
lyophilized powder
Quality Level
specific activity
25-75 units/mg protein
mol wt
~128 kDa (by gel filtration)
composition
Protein, ≥60% biuret
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Research area: Cell Signaling
Glycerol kinase (GK) is part of the FGGY carbohydrate kinase family.
Glycerol kinase (GK) is part of the FGGY carbohydrate kinase family.
Application
Glycerokinase from Cellulomonas sp. has been used:
- for determining the kinetic characteristics of human and trypanosomatid phosphofructokinases using an enzyme-linked kinetic assay.
- to study the effect of sugar in fluorescence emission.
- in 2-Arachidonoylglycerol-based fluorescence assay for DH-463, a fluorescent activity-based probe for monoacylglycerol lipase.
Biochem/physiol Actions
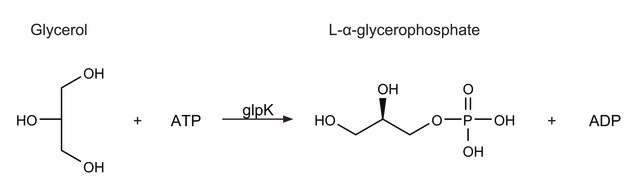
Glycerol kinase catalyzes the MgATP-dependent phosphorylation of glycerol to produce sn-glycerol-3-phosphate and is the rate limiting enzyme in the utilization of glycerol. It is also subject to feedback regulation by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.Mutations in this gene are associated with Glycerol Kinase Deficiency (GKD), a condition characterized primarily by hypertriglyceridemia and hypoglycemia. This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of glycerol and triglyceride when coupled with glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (=G-3-P DH, G3D-301), glycerol-3-phosphate oxidase (=G-3-P oxidase, G3O-301, G3O-311, G3O-321) or pyruvate kinase (PYK-301) and lactate dehydrogenase (LCD-209, LCD-211), lipoprotein lipase (LPL-311, LPL-314) in clinical analysis
Physical properties
Isoelectric point : 4.2
Michaelis constants : 4.4 x 10-5M (Glycerol), 4.3 x 10-4M (ATP)
Inhibitors : p-Chloromercuribenzoate, heavy metal ions (Pb++, Fe++, Hg++, Ag+)
Optimum pH : 9.8 (G-3-PDH system), 7.8 (G-3-P oxidase system) Optimum temperature : 500C
pH Stability : pH 5.5 x 10.0 (25oC, 20hr)
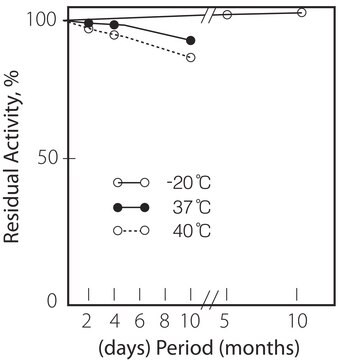
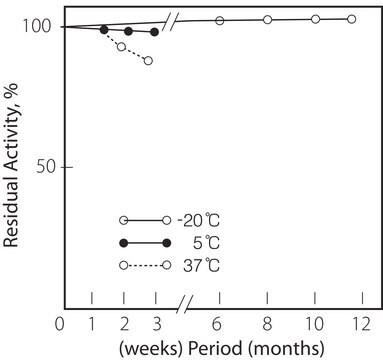
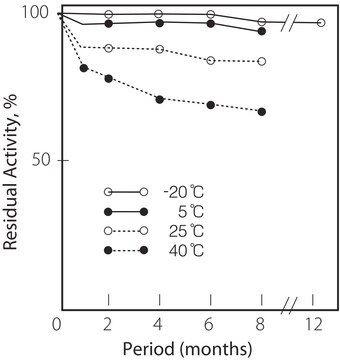
Thermal stability : below 40oC (pH 7.5, 15min)
Substrate specificity : This enzyme catalyzes the stereospecific transfer of the terminal
phosphoryl moiety of ATP to one of the primary hydroxyl group of
glycerol, forming sn-glycerol-3-P. The enzyme has the highest
specificity for glycerol, and also phosphorylates dihydroxyacetone
and glyceraldehyde (Table 1,2). Mg++ is essentially required for the
reaction.
Michaelis constants : 4.4 x 10-5M (Glycerol), 4.3 x 10-4M (ATP)
Inhibitors : p-Chloromercuribenzoate, heavy metal ions (Pb++, Fe++, Hg++, Ag+)
Optimum pH : 9.8 (G-3-PDH system), 7.8 (G-3-P oxidase system) Optimum temperature : 500C
pH Stability : pH 5.5 x 10.0 (25oC, 20hr)
Thermal stability : below 40oC (pH 7.5, 15min)
Substrate specificity : This enzyme catalyzes the stereospecific transfer of the terminal
phosphoryl moiety of ATP to one of the primary hydroxyl group of
glycerol, forming sn-glycerol-3-P. The enzyme has the highest
specificity for glycerol, and also phosphorylates dihydroxyacetone
and glyceraldehyde (Table 1,2). Mg++ is essentially required for the
reaction.
Unit Definition
One unit will convert 1.0 μmole of glycerol and ATP to L-α-glycerophosphate and ADP per min at pH 9.8 at 25 °C in a coupled system with PK/LDH.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing phosphate buffer salts and sodium gluconate
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Peter M Fernandes et al.
The Biochemical journal, 476(2), 179-191 (2018-11-09)
Eukaryotic ATP-dependent phosphofructokinases (PFKs) are often considered unidirectional enzymes catalysing the transfer of a phospho moiety from ATP to fructose 6-phosphate to produce ADP and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. The reverse reaction is not generally considered to occur under normal conditions and
Fei Ying et al.
Scientific reports, 14(1), 3922-3922 (2024-02-17)
The influence of lipid metabolism on tumorigenesis and progression has garnered significant attention. However, the role of Glycerol Kinase (GK), a key enzyme in glycerol metabolism, in Esophageal Carcinoma (ESCA) remains unclear. To further elucidate the relationship between GK and
N Zwaig et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 102(3), 753-759 (1970-06-01)
The activity of glycerol kinase is rate-limiting in the metabolism of glycerol by cells of Escherichia coli. A mutant strain producing a glycerol kinase resistant to inhibition by fructose-1,6-diphosphate grows faster than its wild-type parent on glycerol as the sole
Mitsuko Ohashi-Suzuki et al.
The Journal of veterinary medical science, 73(5), 615-621 (2010-12-29)
African trypanosome species are causative agents for sleeping sickness in humans and nagana disease in cattle. Trypanosoma brucei can generate ATP via a reverse reaction with glycerol kinase (GK) when alternative oxidase (AOX) is inhibited; thus, GK is considered to
N Zwaig et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 153(3737), 755-757 (1966-08-12)
Fructose-1 ,6-diphosphate is a feedback inhibitor of the catabolic enzyme, glycerol kinase, in Escherichia coli. A mutant was isolated which produced a desensitized enzyme. Glucose was no longer as effective in preventing the utilization of exogenous glycerol by cells which
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service