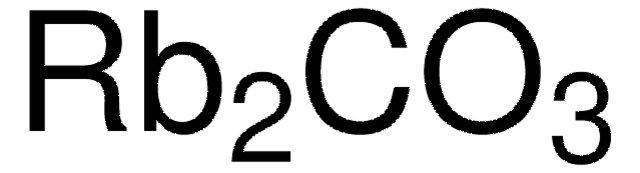267317
Rhenium
foil, thickness 0.25 mm, 99.98% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Rhenium element
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
Re
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
186.21
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12141737
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99.98% trace metals basis
form
foil
description
19.3 μΩ-cm, 20°C
thickness
0.25 mm
bp
5596 °C (lit.)
5627 °C (lit.)
mp
3180 °C (lit.)
density
21.02 g/cm3 (lit.)
SMILES string
[ReH]
InChI
1S/Re
InChI key
WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Rhenium is a very hard, corrosion, and wear-resistant rare metal with ahigh atomic number. It is widely used in the field of catalysis and the preparationof alloys for jet engines.
Application
Rhenium can be used as a working electrode for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reactions.
It can be used as an additive to prepare a molybdenum-titanium-zirconium (TZM) alloy joint to improve its tensile strength.
It can also be used as a catalyst for various hydrodeoxygenation reactions.
It can be used as an additive to prepare a molybdenum-titanium-zirconium (TZM) alloy joint to improve its tensile strength.
It can also be used as a catalyst for various hydrodeoxygenation reactions.
Quantity
3.3 g = 25 × 25 mm; 13.2 g = 50 × 50 mm
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Raphael Horvath et al.
Inorganic chemistry, 52(3), 1304-1317 (2013-01-15)
Transition-metal complexes of the types [Re(CO)(3)Cl(NN)], [Re(CO)(3)py(NN)](+), and [Cu(PPh(3))(2)(NN)](+), where NN = 4,4'-bis(5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-2,2'-bipyridine (OX) and 4,4'-bis(N,N-diphenyl-4-[ethen-1-yl]-aniline)-2,2'-bipyridine (DPA), have been synthesized and characterized. Crystal structures for [Re(CO)(3)Cl(DPA)] and [Cu(PPh(3))(2)(OX)]BF(4) are presented. The crystal structure of the rhenium complex shows a trans
Titel Jurca et al.
Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 19(13), 4278-4286 (2013-02-02)
The development of rhenium(I) chemistry has been restricted by the limited structural and electronic variability of the common pseudo-octahedral products fac-[ReX(CO)3L2] (L2 = α-diimine). We address this constraint by first preparing the bidentate bis(imino)pyridine complexes [(2,6-{2,6-Me2C6H3N=CPh}2C5H3N)Re(CO)3X] (X = Cl 2
Ties J Korstanje et al.
Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 19(39), 13224-13234 (2013-08-16)
Rhenium-based complexes are powerful catalysts for the dehydration of various alcohols to the corresponding olefins. Here, we report on both experimental and theoretical (DFT) studies into the mechanism of the rhenium-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols to olefins in general, and the
Wilber Quispe-Tintaya et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(21), 8668-8673 (2013-04-24)
No significant improvement in therapy of pancreatic cancer has been reported over the last 25 y, underscoring the urgent need for new alternative therapies. Here, we coupled a radioisotope, (188)Rhenium, to an attenuated (at) live Listeria monocytogenes (Listeria(at)) using Listeria-binding
Jonathan M Smieja et al.
Inorganic chemistry, 52(5), 2484-2491 (2013-02-20)
Electrocatalytic properties, X-ray crystallographic studies, and infrared spectroelectrochemistry (IR-SEC) of Mn(bpy-tBu)(CO)3Br and [Mn(bpy-tBu)(CO)3(MeCN)](OTf) are reported. Addition of Brönsted acids to CO2-saturated solutions of these Mn complexes and subsequent reduction of the complexes lead to the stable and efficient production of
Articles
Combinatorial Materials Science identifies breakthrough materials through systematic exploration, aiding material discovery.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service