926434
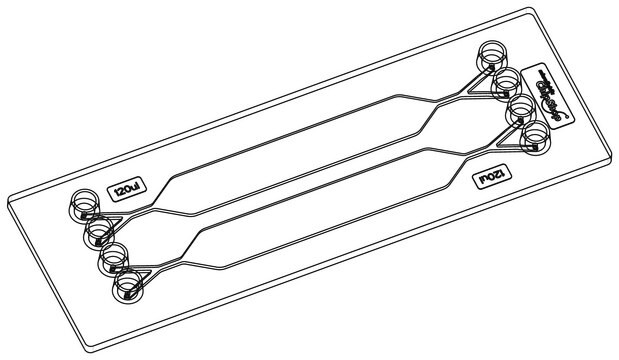
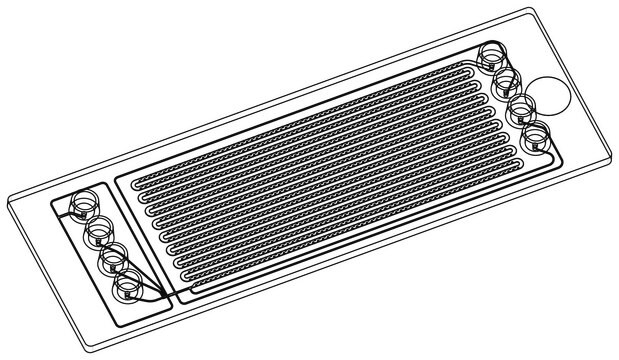
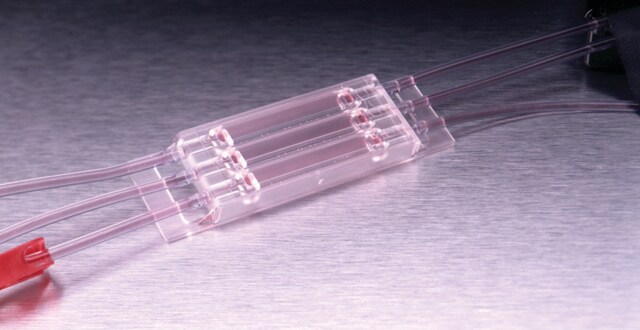
Finger Pump Mixer Chip
Fluidic 999, COP
Synonym(s):
Microfluidic chip
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
42142600
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
description
Microfludic chip x1
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
The Finger Pump Mixer 999 COP microfluidic chip applies active mixing principles by integrating a finger pump and a variety of features counteracting the laminar flow to generate mixtures with a wider range of mixing ratios that are not feasible with passive mixing devices.
Features and Benefits
- One micromixing unit per chip
- The mixing of up to three liquids is facilitated by the pearl-chain unit
- The structures of the pearl-chain unit increase lateral velocity to enhance mixing
- An integrated figure pump is used to displace air and move liquid back and forth in the channel system which improves mixing by allowing long co-flow
- The integrated pump can either be actuated by hand or controlled and automated with a suitable actuator
Components
Chip Properties:
- Mini Luer Interface
- Material: Cyclic olefin polymer (COP)
- Chamber Volumes: 27 μl, 38 μl, 330 μl
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Dongfei Liu et al.
Lab on a chip, 17(11), 1856-1883 (2017-05-10)
The microfluidic technique has brought unique opportunities toward the full control over the production processes for drug delivery carriers, owing to the miniaturisation of the fluidic environment. In comparison to the conventional batch methods, the microfluidic setup provides a range
Sharma T Sanjay et al.
Advanced drug delivery reviews, 128, 3-28 (2017-09-19)
Conventional systematically-administered drugs distribute evenly throughout the body, get degraded and excreted rapidly while crossing many biological barriers, leaving minimum amounts of the drugs at pathological sites. Controlled drug delivery aims to deliver drugs to the target sites at desired
Articles
Microfluidic assembly improves polyamine nanoencapsulation of nucleic acids, overcoming challenges like polydispersity and poor reproducibility.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service