D26202
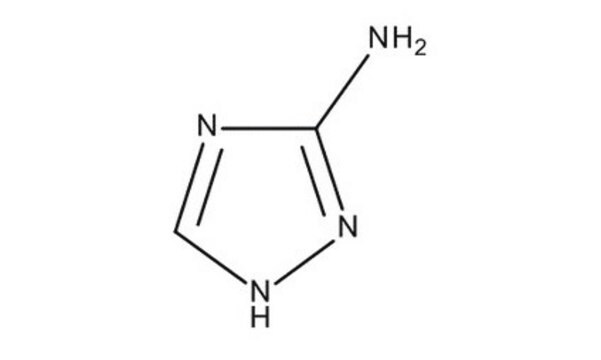
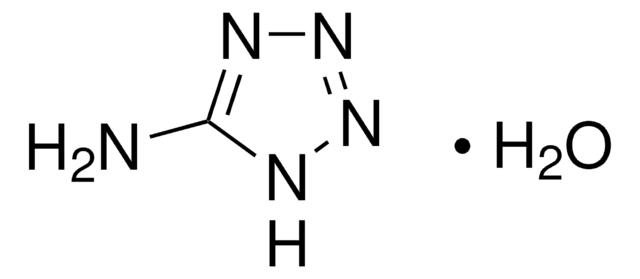
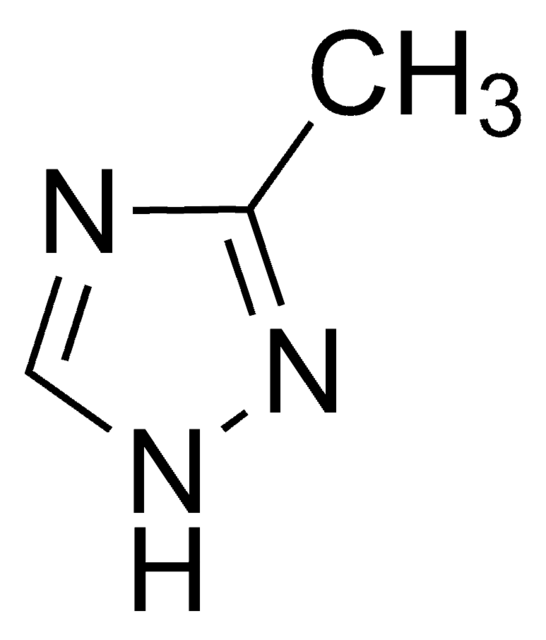
3,5-Diamino-1,2,4-triazole
98%
Synonym(s):
Guanazole
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C2H5N5
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
99.09
Beilstein:
112467
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
form
solid
mp
202-205 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Nc1n[nH]c(N)n1
InChI
1S/C2H5N5/c3-1-5-2(4)7-6-1/h(H5,3,4,5,6,7)
InChI key
PKWIYNIDEDLDCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
3,5-Diamino-1,2,4-triazole, also known as Guanazole is a heterocyclic compound and is commonly used as a building block in the synthesis of gallium complexes of tert-butyl-substituted acyclic and cyclic compounds. It is also being investigated as a corrosion inhibitor for copper.
Application
Inhibitor of DNA synthesis.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Repr. 2 - STOT RE 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Inhibition of ribonucleotide reductases encoded by herpes simplex viruses.
T Spector
Pharmacology & therapeutics, 31(3), 295-302 (1985-01-01)
G Tipples et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 173(16), 4932-4940 (1991-08-01)
Chlamydiae are obligate intracellular bacteria that are dependent on eukaryotic host cells for ribonucleoside triphosphates but not deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates. Ribonucleotide reductase is the only enzyme known to catalyze the direct conversion of a ribonucleotide to a deoxyribonucleotide. Hydroxyurea inhibits ribonucleotide
A A Alhaider et al.
Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 71(1), 89-94 (1982-01-01)
A series of guanazole prodrugs, which are less water soluble than the parent compound and have relatively higher molecular weights, was recently synthesized, and their antineoplastic activities were measured in vitro. In present work, the ionization constants and partition coefficients
Studies on the selective toxicity of guanazole in mice.
C Dave et al.
European journal of cancer, 14(1), 33-40 (1978-01-01)
[Pharmacokinetics of antitumor drugs].
V A Filov et al.
Voprosy onkologii, 29(7), 3-13 (1983-01-01)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service