H3003
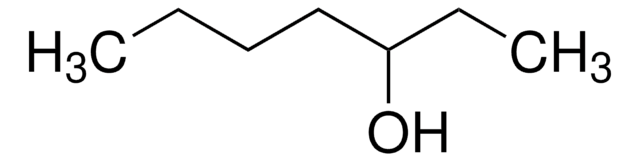
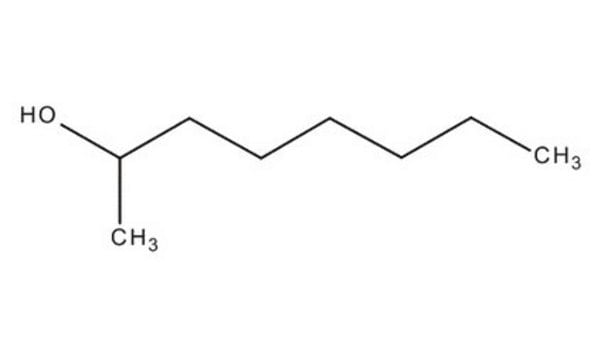
2-Heptanol
98%
Synonym(s):
Methyl pentyl carbinol
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH3(CH2)4CH(OH)CH3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
116.20
Beilstein:
1719088
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
refractive index
n20/D 1.420 (lit.)
bp
160-162 °C (lit.)
density
0.817 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CCCCCC(C)O
InChI
1S/C7H16O/c1-3-4-5-6-7(2)8/h7-8H,3-6H2,1-2H3
InChI key
CETWDUZRCINIHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
2-Heptanol is an aliphatic secondary alcohol. It can undergo selective oxidation to form the corresponding ketone in the presence of a novel Pd catalyst supported on amphiphilic carbon nanotubes. The distribution coefficient of 2-heptanol between micelles and water indicates that it is solubilized both at the surface and in the interior of the micelles.
Application
2-Heptanol in combination with dimethyl sulfoxide form a porogenic mixture that may be used produce macroporous poly (acrylamide-co-N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide) monolithics via copolymerization.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
138.2 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
59 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Solubilization of heptanols and a, ?-alkanediols in aqueous solutions of sodium dodecyl sulfate.
Blokhus AM, et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 114(1), 9-15 (1986)
Green alcohol oxidation on palladium catalysts supported on amphiphilic hybrid carbon nanotubes.
Benyounes A, et al.
Catalysis Today, 249, 137-144 (2015)
Preparation of porous hydrophilic monoliths: Effect of the polymerization conditions on the porous properties of poly (acrylamide-co-N, N'-methylenebisacrylamide) monolithic rods.
Xie S, et al.
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 5(6), 1013-1021 (1997)
David J S Patinha et al.
Polymers, 12(9) (2020-08-28)
In this contribution, thin poly(ionic liquid) (PIL) coatings with a well-defined pore structure built up from interpolyelectrolyte complexation between a PIL and poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) were successfully used for enhanced solid phase microextraction (SPME). The introduction of porosity with tunable
David J S Patinha et al.
Talanta, 198, 193-199 (2019-03-17)
In this work, a facile preparation of SPME fibers with increased surface area is presented. The SPME fibers were prepared by grinding poly(ionic liquids) (PILs) to obtain particles of 1-16 µm and, with the aid of a silicon adhesive, attach these
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service