AB3542
Anti-Monocarboxylate Transporter 2 Antibody
serum, Chemicon®
Synonym(s):
MCT2
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
NACRES:
NA.41
clone:
polyclonal
application:
ELISA
WB
WB
species reactivity:
rat
technique(s):
ELISA: suitable
western blot: suitable
western blot: suitable
citations:
10
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
antibody form
serum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
species reactivity
rat
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
western blot: suitable
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... SLC16A7(9194)
Specificity
Recognizes rat Monocarboxylate Transporter 2 (MCT2). The immunogen shows no significant sequence homology with other MCT.
The immunogen sequence is 93% conserved in mouse and 66% in hamster. Reactivity with other species has not been confirmed.
The immunogen sequence is 93% conserved in mouse and 66% in hamster. Reactivity with other species has not been confirmed.
Immunogen
A 15 amino acid peptide sequence near the C-terminus of rat MCT2 (Jackson et al. 1997; Dao et al. 1998; Koehler-Stec et al. 1998; Price et al. 1998; Halestrap & Price 1999).
Application
Anti-Monocarboxylate Transporter 2 Antibody is an antibody against Monocarboxylate Transporter 2 for use in ELISA & WB.
Research Category
Neuroscience
Neuroscience
Research Sub Category
Ion Channels & Transporters
Ion Channels & Transporters
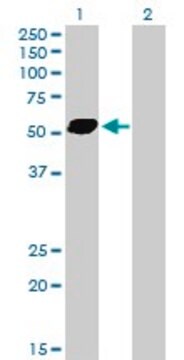
Western blot
ELISA: 1:10,000-1:100,000 using 50-100 ng control peptide (Catalog number AG218) per well.
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by the end user.
ELISA: 1:10,000-1:100,000 using 50-100 ng control peptide (Catalog number AG218) per well.
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by the end user.
Linkage
Replaces: AB3542P
Physical form
Rabbit serum. Liquid.
Storage and Stability
Maintain at -20°C in undiluted aliquots for up to 6 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Legal Information
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Estrogen Receptor Involvement in Noradrenergic Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Glucoregulatory Neurotransmitter and Stimulus-Specific Glycogen Phosphorylase Enzyme Isoform Expression.
A S M H Mahmood et al.
ASN neuro, 12, 1759091420910933-1759091420910933 (2020-04-03)
E M England et al.
Journal of animal science, 95(8), 3552-3562 (2017-08-15)
Acute activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) increases monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) expression in skeletal muscle. However, the impact of chronic activation of AMPK on MCT expression in skeletal muscle is unknown. To investigate, MCT1, MCT2, and MCT4 mRNA expression and
J S Gilbert et al.
Placenta, 33(2), 100-105 (2011-12-22)
While utero-placental insufficiency is associated with adverse outcomes for both mother and fetus, many of the maternal-fetal adaptations during pregnancy in models of fetal compromise remain unclear. The purpose of this study was to determine if chronically reduced uterine perfusion
Estrogen Receptor Involvement in Noradrenergic Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Glucoregulatory Neurotransmitter and Stimulus-Specific Glycogen Phosphorylase Enzyme Isoform Expression.
A S M H Mahmood et al.
ASN neuro, 12, 1759091420910933-1759091420910933 (2020-04-03)
Emmanuel Cruz et al.
Glia, 70(11), 2207-2231 (2022-08-03)
The consumption of glucose in the brain peaks during late childhood; yet, whether and how glucose metabolism is differentially regulated in the brain during childhood compared to adulthood remains to be understood. In particular, it remains to be determined how
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service