MAB5324
Anti-Polysialic Acid-NCAM Antibody, clone 2-2B
ascites fluid, clone 2-2B, Chemicon®
Synonym(s):
PSA-NCAM
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
ascites fluid
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
2-2B, monoclonal
species reactivity
mouse, rat, vertebrates, human
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
radioimmunoassay: suitable
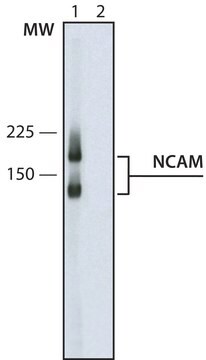
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgM
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... NCAM1(4684)
General description
The broadest expression of PSA occurs on precursor cells during early development and plays a role in promotion of the migration of these cells after cell division. In most cases, PSA expression is lost after the migration process is completed. However, the axons of neurons often retain PSA to bundle,sprout, and branch appropriately during axon path-finding.
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
Immunocyto/histochemistry: A 1:200-1:400 dilution of a previous lot of this antibody worked on live and fixed cells, tissue sections either frozen or fixed with any kind of fixative. (Rougon et al., 1986; Theodosis et al., 1991, 1999). It is not recommend that the antibody be used on paraffin embedded tissue since it gives variable results.
Radioimmunoassay (RIA) :
A previous lot of this antibody was used in RIA. (Figarella-Branger et al., 1996)
Cell sorting and cell panning (Ben-Hur et al., 1998)
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Quality
Immunohistochemistry(paraffin) Analysis:
PSA-NCAM (cat. # MAB5324) representative staining pattern/morphology on human hippocampus. Tissue pretreated with EDTA pH 8, antigen retrieval. Antibody was diluted to 1:100, using IHC-Select Detection with HRP-DAB. Immunoreactivity is seen as plasma membrane staining in neurons.
Optimal Staining With Epitope Retrieval: Alzheimer’s Hippocampus
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Handling Recommendations: Upon receipt, and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgM and affect product performance. Note: Variability in freezer temperatures below -20°C may cause glycerol containing solutions to become frozen during storage.
Analysis Note
Positive control tissue: Young Rat Hippocampus, human hippocampus.
Other Notes
Legal Information
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
recommended
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service