38266
Ferrioxamine E from Streptomyces antibioticus
suitable for microbiology, ≥95%
Synonym(s):
1,12,23-Trihydroxy-1,6,12,17,23,28-hexaazacyclotritriacontane-2,5,13,16,24,27-hexone Iron(III) complex
About This Item
Recommended Products
sterility
non-sterile
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
≥95%
form
powder
loss
≤6% loss on drying
application(s)
environmental
food and beverages
microbiology
storage temp.
2-8°C
suitability
Salmonella spp.
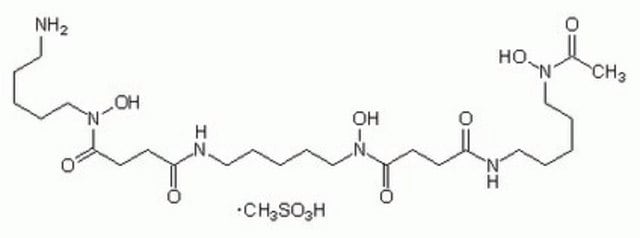
SMILES string
[Fe+3].[O-]N1CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N([O-])CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N([O-])CCCCCNC(=O)CCC1=O
InChI
1S/C27H45N6O9.Fe/c34-22-10-14-26(38)32(41)20-8-3-6-18-30-24(36)12-15-27(39)33(42)21-9-2-5-17-29-23(35)11-13-25(37)31(40)19-7-1-4-16-28-22;/h1-21H2,(H,28,34)(H,29,35)(H,30,36);/q-3;+3
InChI key
MZFKJKOHYACYNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Ferrioxamine E from Streptomyces antibioticum is a siderophore which facilitates the supply of iron (III), an essential trace element, to bacteria involved in food poisoning, including Salmonella, Enterobacter saka-zakii and Yersinia enterocolitica. It promotes rapid growth by reducing the lag phase in culture media and reactivates dormant bacteria. Use of ferrioxamine E can permit rapid detection of low bacterial cell counts, even from dry products like spices and tea after long storage periods. It is an essential component of quality control efforts in the food industry.
Ferrioxamine E is often used in Buffered Peptone Water, the medium recommended by the ISO-Norms for Enterobacteriacea. Ferrioxamine E also improves the motility of Salmonella, which helps to improve the identification by semisolid selective motility media like SIM, MRSV, DIASSALM or SMS. Ferrioxamine E does not improve growth of Escherichia coli, Shigella, Proteus, Providencia and Morganella species; a feature that makes it a semi-selective compound. The recommended concentration of Ferrioxamine E to promote bacterial growth is between 5 and 200 ng/mL
Application
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Microbiological assessment of bacteria found in spices, a potent source for food spoilage and pathogens.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service