72910
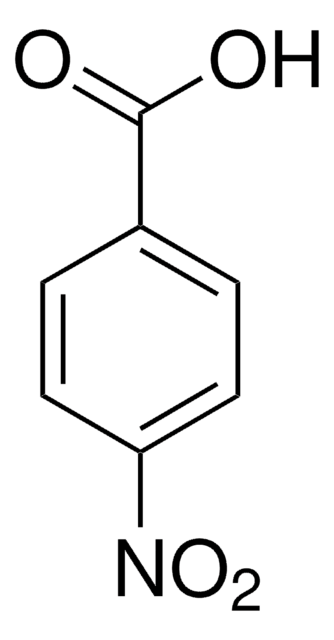
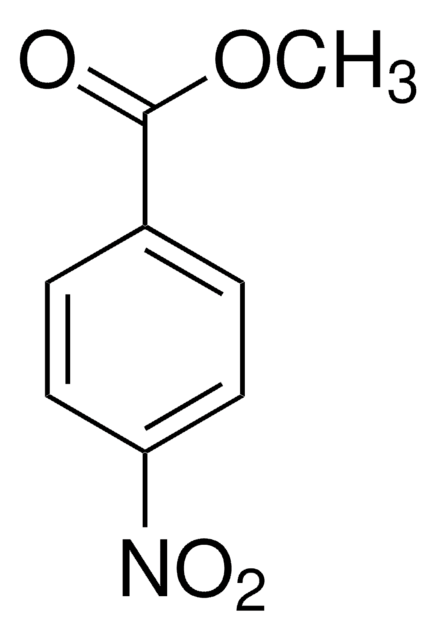
4-Nitrobenzoic acid
purum, ≥98.0% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
p-Nitrobenzoic acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
O2NC6H4CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
167.12
Beilstein:
973593
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
grade
purum
Quality Level
Assay
≥98.0% (HPLC)
form
crystals
mp
237-240 °C (lit.)
239-242 °C
functional group
carboxylic acid
nitro
SMILES string
OC(=O)c1ccc(cc1)[N+]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C7H5NO4/c9-7(10)5-1-3-6(4-2-5)8(11)12/h1-4H,(H,9,10)
InChI key
OTLNPYWUJOZPPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
4-Nitrobenzoic acid can be used:
- As a co-catalyst with thioxotetrahydropyrimidinone for the α-alkylation of ketones.
- For the synthesis of mononuclear zinc carboxylate complexes by reacting with zinc sulfate heptahydrate and NaOH.
- As an additive in the room temperature catalytic Wittig reaction.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Muta. 2 - Repr. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Enantioselective Organocatalytic ?-Alkylation of Ketones by SN1-Type Reaction of Alcohols.
Trifonidou M and Kokotos CG
European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2012(8), 1563-1568 (2012)
Synthesis and characterization of zinc benzoate complexes through combined solid and solution phase reactions.
Karmakar A and Baruah JB
Polyhedron, 27(17), 3409-3416 (2008)
Breaking the ring through a room temperature catalytic Wittig reaction.
O'Brien CJ, et al.
Chemistry?A European Journal , 19(19), 5854-5858 (2013)
C L Leverette et al.
Applied spectroscopy, 60(8), 906-913 (2006-08-24)
Preferentially aligned silver nanorod arrays prepared by oblique angle vapor deposition were evaluated as substrates for surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA) spectroscopy. These nanorod arrays have an irregular surface lattice and are composed of tilted, cylindrically shaped nanorods that have an
M A Hughes et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 183(4), 1225-1232 (2001-02-07)
Pseudomonas putida strain TW3 is able to metabolize 4-nitrotoluene via 4-nitrobenzoate (4NBen) and 3, 4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (protocatechuate [PCA]) to central metabolites. We have cloned, sequenced, and characterized a 6-kbp fragment of TW3 DNA which contains five genes, two of which
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service