H4628
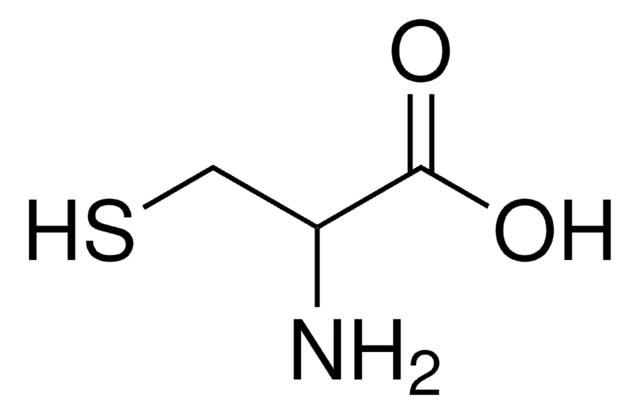
DL-Homocysteine
≥95% (titration)
Synonym(s):
2-Amino-4-mercaptobutyric acid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
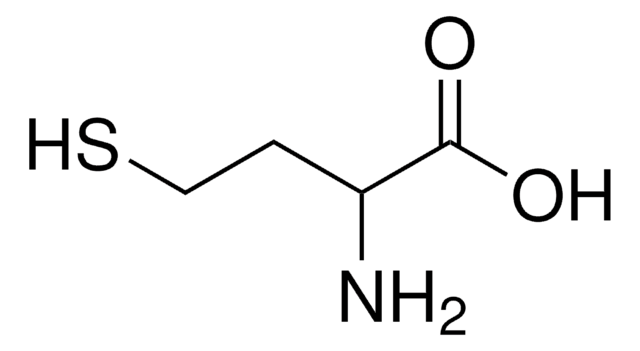
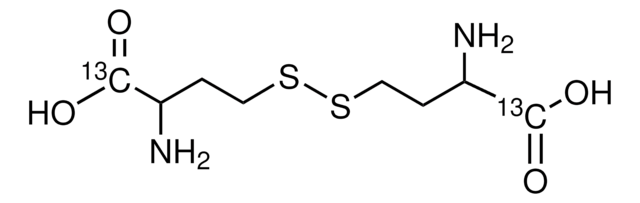
HSCH2CH2CH(NH2)COOH
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
135.18
Beilstein:
1721683
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
eCl@ss:
42021308
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
Product Name
DL-Homocysteine, ≥95% (titration)
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (titration)
form
powder
mp
232-233 °C (lit.)
solubility
H2O: soluble
application(s)
cell analysis
peptide synthesis
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
NC(CCS)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H9NO2S/c5-3(1-2-8)4(6)7/h3,8H,1-2,5H2,(H,6,7)
InChI key
FFFHZYDWPBMWHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
DL-Homocysteine has been used to induce hyperhomocysteinemia in Sprague–Dawley rats. It has also been used to study the effects of hyperhomocysteinemia on atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Homocysteine is a sulfhydryl-containing amino acid, synthesized from methionine. It is a non-essential, non-proteinogenic amino acid. It is an important determinant of the methylation cycle and is present in the plasma in four forms. An abnormally high level of homocysteine leads to hyperhomocysteinemia and also promotes atherosclerosis.
Increased plasma homocysteine is a risk factor for coronary heart disease and carcinogenesis; may be a marker for tumor cell growth.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
The Molecular and Cellular Effect of Homocysteine Metabolism Imbalance on Human Health
Henrieta S
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(10), 1733-1733 (2016)
Hyperhomocysteinemia decreases bone blood flow
Neetu Tyagi
Vascular Health, 7, 31-35 (2011)
Homocysteine: role and implications in atherosclerosis.
Guthikonda S and Haynes WG
Current Atherosclerosis Reports, 8(2), 100-106 (2006)
Role of homocysteine in the development of cardiovascular disease
Paul Ganguly and Sreyoshi Fatima Alam
Nutrition Journal, 14(6) (2015)
Effects of vitamin supplementation and hyperhomocysteinemia on atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice
Ji Zhou
Atherosclerosis, 168(2), 255-262 (2003)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service