N8505
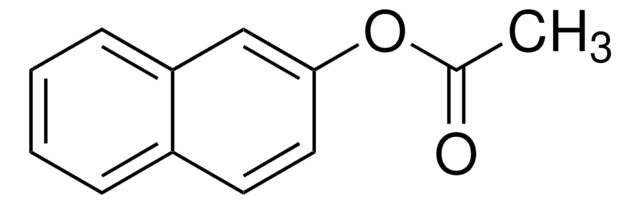
1-Naphthyl acetate
≥98% (C)
Synonym(s):
α-Naphthyl acetate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH3CO2C10H7
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
186.21
Beilstein:
2046403
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% (C)
form
crystals
mp
43-46 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
CC(=O)Oc1cccc2ccccc12
InChI
1S/C12H10O2/c1-9(13)14-12-8-4-6-10-5-2-3-7-11(10)12/h2-8H,1H3
InChI key
VGKONPUVOVVNSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
1-Naphthyl acetate is a 1-napthyl ester. Mechanism of photo-Fries rearrangement of 1-naphthyl acetate has been studied using steady state photolysis and laser flash photolysis. Kinetics of photo-Fries rearrangement of 1-napthyl acetate has been studied using steady-state, time-resolved chemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization (CIDNP) and flash photolysis methods.
Application
1-Naphthyl acetate may be used in a rapid staining method for identification of macrophages; counts by this method were confirmed by the more complex morphological criteria, by phagocytosis, and by the presence of Fc receptors. It may be employed as substrate to investigate the distribution of non-specific carboxylic esterases (EC 3.1.1) in the digestive tract of perch, Perm fliiviatilis L.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
235.4 °F
Flash Point(C)
113 °C
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Magnetic isotope and external magnetic field effects upon the photo-Fries rearrangement of 1-naphthyl acetate.
Nakagaki R, et al.
The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 89(15), 3222-3226 (1985)
Non-specific carboxylic esterase activity in the digestive tract of the perch, Perca fluviatilis L.
Hirji KN and Courtney WAM.
Journal of Fish Biology, 22(1), 1-7 (1983)
Laser flash photolysis and CIDNP studies of 1-naphthyl acetate photo-Fries rearrangement.
Gritsan NP, et al.
The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 100(11), 4448-4458 (1996)
Juan C Sanchez-Hernandez et al.
Comparative biochemistry and physiology. Toxicology & pharmacology : CBP, 150(4), 503-511 (2009-08-05)
Carboxylesterases (CbEs) are key enzymes in pesticide detoxification. These esterases are involved in the biochemical mechanism for pesticide resistance in some pest species, and further they are considered an efficient protective mechanism against acute toxicity by organophosphate (OP) pesticides in
Anchalee Prasansuklab et al.
BMC complementary and alternative medicine, 18(1), 223-223 (2018-07-26)
Streblus asper is a well-known plant native to Southeast Asia. Different parts of the plant have been traditionally used for various medicinal purposes. However, there is very little scientific evidence reporting its therapeutic benefits for potential treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Articles
Quantum dots (QDs): Semiconductor nanoparticles with diverse applications including displays, lighting, and biomedical imaging.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service