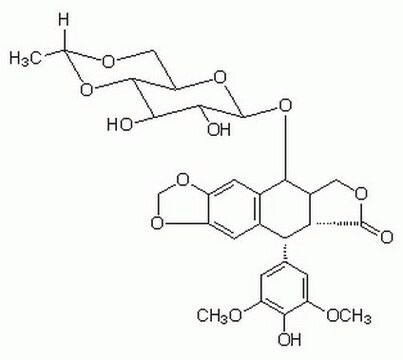
S6942
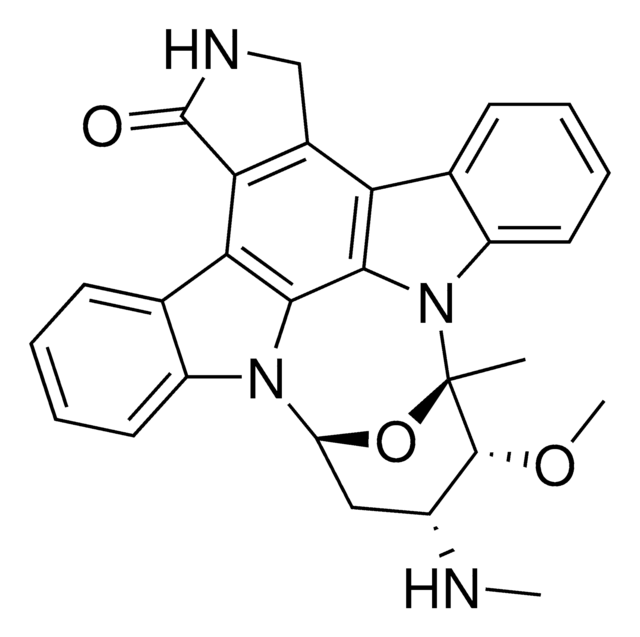
Staurosporine
from Streptomyces sp., >98% (HPLC), solution, protein kinase inhibitor
Synonym(s):
Antibiotic AM-2282
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Staurosporine solution from Streptomyces sp., Ready Made Solution, 1 mM in DMSO (100 μg/214 μL), 0.2 μm filtered
Quality Level
sterility
0.2 μm filtered
Assay
>98% (HPLC)
concentration
1 mM in DMSO (100 μg/214 μL)
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
antibiotic activity spectrum
fungi
Mode of action
enzyme | inhibits
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
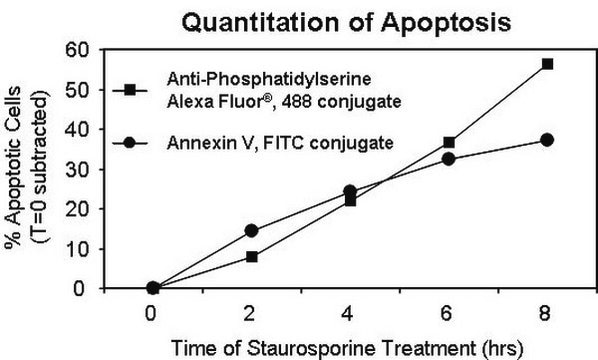
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
188.6 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
87 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Protein-based drug transporters are expressed in Sf9 cells. Understanding the specific mechanisms of tumor cell transporters is an essential aspect of chemotherapeutic drug design.
DISCOVER Bioactive Small Molecules for Nitric Oxide & Cell Stress Research
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service