All Photos(1)
About This Item
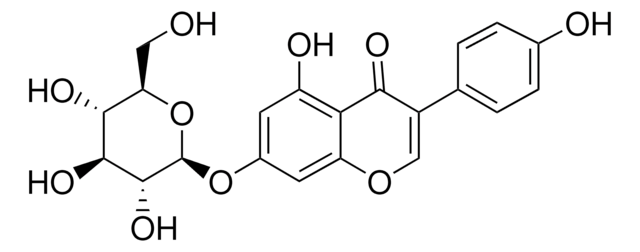
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C33H59N11O11
Molecular Weight:
785.89
UNSPSC Code:
51111800
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
form
lyophilized
composition
Peptide Content, ≥75%
storage condition
protect from light
storage temp.
−20°C
Amino Acid Sequence
Pro-Ala-Ala-Thr-Ala-Arg-Leu-Ser
Application
Kisspeptins are a family of peptides encoded by the KISS-1 gene that are involved in GPR54 mediated cell signaling. Kiss-1 gene products are involved in metastasis suppression and the regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion. A variety of kisspeptin peptides are available for use to study their unique functions.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Jenny Clarkson et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 28(35), 8691-8697 (2008-08-30)
Kisspeptin and its receptor GPR54 have recently been identified as key signaling partners in the neural control of fertility in animal models and humans. The gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons represent the final output neurons of the neural network controlling fertility
E Papaoiconomou et al.
In vivo (Athens, Greece), 25(3), 343-354 (2011-05-18)
The Kiss-1 gene encodes a secreted protein that is proteolytically cleaved to produce a number of structurally related peptides, with high interspecies conservation, globally termed kisspeptins. The original niche for the role of kisspeptin in human physiology is derived from
Rafael Pineda et al.
Progress in brain research, 181, 55-77 (2010-05-19)
Reproductive maturation and function are maintained by a complex neurohormonal network that integrates at the so-called hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. This system is hierarchically controlled by the decapeptide, GnRH, which in turn is under the dynamic regulation of multiple stimulatory and
Naresh Kumar Hanchate et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 32(3), 932-945 (2012-01-21)
Reproduction is controlled in the brain by a neural network that drives the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Various permissive homeostatic signals must be integrated to achieve ovulation in mammals. However, the neural events controlling the timely activation of GnRH
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service