SRP6057
Activin A from mouse
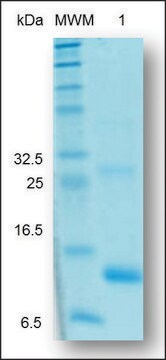
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥95% (SDS-PAGE), ≥95% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
FRP, FSH-releasing protein, Inhibin beta-1
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized
mol wt
26.2 kDa
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
technique(s)
cell culture | embryo: suitable
NCBI accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
mouse ... INHBA(3624)
General description
Activin A is a member of the TGF (transforming growth factor)-β family of proteins produced by many cell types throughout development. Mouse Activin A has 100% amino acid sequence identity to human, rat, porcine, bovine and feline proteins. Recombinant mouse Activin A is a nonglycosylated homodimer, containing two 117 amino acid chains, with a total molecular weight of 26.2 kDa.
Application
Activin A has been used:
- to induce differentiation of embryonic stem cells to pancreatic β cells
- in the induction of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to insulin-producing cells
- to induce endoderm differentiation from human embryonic stem cells
- as a component of β cell induction medium.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Activins interact with Type I and Type II serine/threonine kinases to signal to SMAD proteins to regulate a variety of functions, including cell proliferation, differentiation, wound healing, apoptosis, metabolism, etc. Activin A is a homodimer of two β A chains and is not biologically active until the N terminal propeptide is cleaved from each chain. Activin A is involved in mesoderm formation and hematopoietic development.
Physical form
Recombinant mouse Activin A is lyophilized with 0.02% TFA.
Preparation Note
Centrifuge the vial prior to opening.
Reconstitution
Centrifuge vial before opening. When reconstituting the product, gently pipet and wash down the sides of the vial to ensure full recovery of the protein into solution. It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized product with sterile water, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions.
Other Notes
MGLECDGKVN ICCKKQFFVS FKDIGWNDWI IAPSGYHANY CEGECPSHIA GTSGSSLSFH STVINHYRMR GHSPFANLKS CCVPTKLRPM SMLYYDDGQN IIKKDIQNMI VEECGCS
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
In vitro derivation of functional insulin-producing cells from human embryonic stem cells.
Jiang W
Cell Research, 17, 333-344 (2007)
Inducing embryonic stem cells to differentiate into pancreatic beta cells by a novel three-step approach with activin A and all-trans retinoic acid.
Shi Y
Stem Cells, 23, 656-662 (2005)
Requirement for activin A and transforming growth factor--beta 1 pro-regions in homodimer assembly.
Gray AM
Science, 247, 1328-1330 (1990)
Differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from diabetic patients into insulin-producing cells in vitro.
Sun Y
Chinese Medical Journal (English Edition), 120, 771-776 (2007)
Different phenotypes for mice deficient in either activins or activin receptor type II.
Matzuk MM
Nature, 374, 356-360 (1995)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service