137502
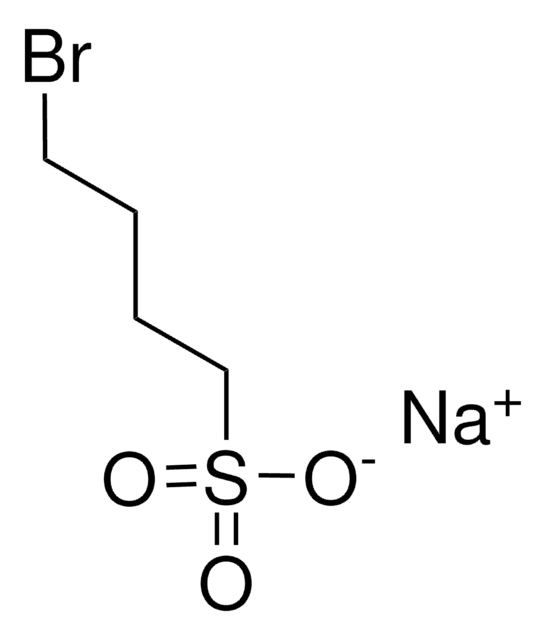
Sodium 2-bromoethanesulfonate
98%
Synonym(s):
2-Bromoethanesulfonic acid sodium salt
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
BrCH2CH2SO3Na
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
211.01
Beilstein:
4590828
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
mp
283 °C (dec.) (lit.)
solubility
water: soluble 100 mg/mL, clear, colorless
functional group
bromo
sulfonic acid
SMILES string
[Na+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)CCBr
InChI
1S/C2H5BrO3S.Na/c3-1-2-7(4,5)6;/h1-2H2,(H,4,5,6);/q;+1/p-1
InChI key
HNFOAHXBHLWKNF-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Sodium 2-bromoethanesulfonate acts as methanogenesis inhibitor during anaerobic digestion. It reacts with lithium sulfinated polysulfones(PSU) to yield sulfoethylated PSU.
Application
Sodium 2-bromoethanesulfonate(BES) was used to investigate the effect of BES on inhibition of bacterial growth.
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Meike Goenrich et al.
Journal of biological inorganic chemistry : JBIC : a publication of the Society of Biological Inorganic Chemistry, 9(6), 691-705 (2004-09-15)
Methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) catalyses the reduction of methyl-coenzyme M (CH(3)-S-CoM) with coenzyme B (HS-CoB) to methane and CoM-S-S-CoB. It contains the nickel porphyrinoid F(430) as prosthetic group which has to be in the Ni(I) oxidation state for the enzyme
Jeffrey M Boyd et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 188(23), 8062-8069 (2006-09-26)
Bacterial growth with short-chain aliphatic alkenes requires coenzyme M (CoM) (2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid), which serves as the nucleophile for activation and conversion of epoxide products formed from alkene oxidation to central metabolites. In the present work the CoM analog 2-bromoethanesulfonate (BES)
F J Cervantes et al.
Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 64(5), 702-711 (2004-02-06)
The impact of humic acids and the humic model compound, anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS), on the biodegradation of carbon tetrachloride (CT) by anaerobic granular sludge was studied. Addition of both humic acids and AQDS at sub-stoichiometric levels increased the first-order rate of
Kewei Xu et al.
Bioresource technology, 101(8), 2600-2607 (2009-11-27)
In this study, the microbial response of anaerobic sludge digestion to the addition of two classic methanogenic inhibitors (chloroform, 2-bromoethanesulfonate) was investigated. Both the toxicants showed their effectiveness on CH(4) production, whereas the hydrogen responses and acetate accumulations were elicited
S Venkata Mohan et al.
Bioresource technology, 99(1), 59-67 (2007-01-26)
Influence of different pretreatment methods applied on anaerobic mixed inoculum was evaluated for selectively enriching the hydrogen (H(2)) producing mixed culture using dairy wastewater as substrate. The experimental data showed the feasibility of molecular biohydrogen generation utilizing dairy wastewater as
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service