14960
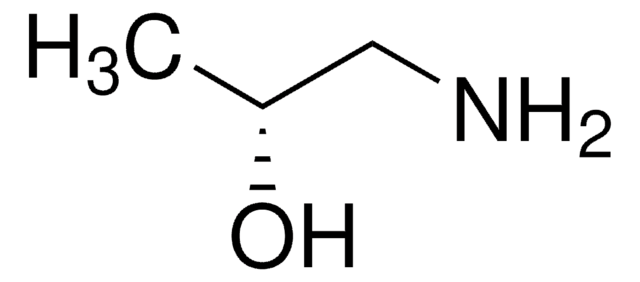
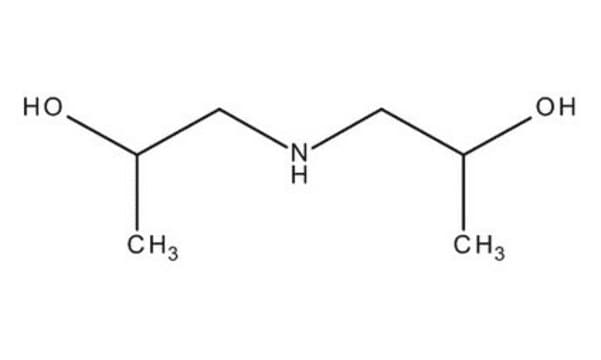
Bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine
≥98.0% (T)
Synonym(s):
1,1′-Iminodi-2-propanol, Diisopropanolamine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
NH[CH2CH(OH)CH3]2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
133.19
Beilstein:
605363
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98.0% (T)
form
solid
impurities
≤1% water
bp
249-250 °C/745 mmHg (lit.)
mp
42-45 °C (lit.)
solubility
H2O: miscible
alcohol: miscible
density
1.004 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
functional group
amine
hydroxyl
SMILES string
CC(O)CNCC(C)O
InChI
1S/C6H15NO2/c1-5(8)3-7-4-6(2)9/h5-9H,3-4H2,1-2H3
InChI key
LVTYICIALWPMFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
Bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine (Diisopropanolamine) was used to study its effects upon choline uptake and phospholipid synthesis in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
275.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
135 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Two cases of contact dermatitis due to diisopropanolamine.
Yoshihiro Umebayashi
The Journal of dermatology, 32(2), 145-146 (2005-05-24)
W T Stott et al.
Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 46(2), 761-766 (2007-11-09)
Aminoalcohols differ in mammalian toxicity at least in part based upon their ability to alter the metabolism of phospholipids and to cause depletion of the essential nutrient choline in animals. This study examined the incorporation of diisopropanolamine (DIPA) into phospholipids
S A Saghir et al.
Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 45(10), 2047-2056 (2007-06-23)
This study was conducted to determine the relative dermal bioavailability (absorption), distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of diisopropanolamine (DIPA), an alcohol amine used in a number of industrial and personal care products. Groups of 4 female Fischer 344 rats received
L M Gieg et al.
Canadian journal of microbiology, 45(5), 377-388 (1999-08-14)
Diisopropanolamine (DIPA) is a "sweetening agent" used to remove hydrogen sulfide from sour natural gas, and it is a contaminant at some sour gas treatment facilities in western Canada. To investigate the biodegradation of this alkanolamine, 14C-DIPA was used in
K A Johnson et al.
Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 45(10), 1838-1845 (2007-05-18)
The repeated dose oral and dermal toxicity of diisopropanolamine (DIPA) was evaluated in rats and compared to the reported toxicity of the related secondary alcohol amine, diethanolamine (DEA). Fischer 344/DuCrl rats were given up to 750 mg/kg/day by dermal application
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service


![1-[N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-2-propanol 94%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/219/539/52108f19-e9a0-4987-b605-9969a5cc720d/640/52108f19-e9a0-4987-b605-9969a5cc720d.png)