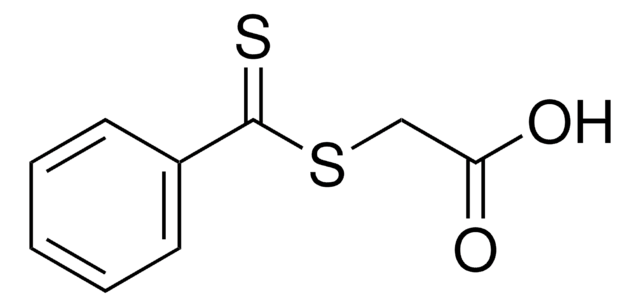
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
>95% (HPLC)
form
solid
mp
94-96 °C
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
S=C(SSC(=S)c1ccccc1)c2ccccc2
InChI
1S/C14H10S4/c15-13(11-7-3-1-4-8-11)17-18-14(16)12-9-5-2-6-10-12/h1-10H
InChI key
LWGLGSPYKZTZBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
RAFT polymerization uses commercial agents to control polymer properties without cytotoxic heavy metals like ATRP.
RAFT polymerization offers living characteristics to radical polymerization, contributing versatility to reversible deactivation radical polymerization methods.
Micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization.
Protocols
RAFT polymerization offers precise control, enabling tailored synthesis of complex polymer structures.
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
We present an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Polymerization via ATRP procedures demonstrated by Prof. Dave Haddleton's research group at the University of Warwick.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service





![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)