219361
Anti-Cathepsin D Rabbit pAb
liquid, Calbiochem®
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.43
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
antibody form
saturated ammonium sulfate (SAS) precipitated
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
liquid
contains
≤0.1% sodium azide as preservative
species reactivity
human
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
isotype
IgG
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
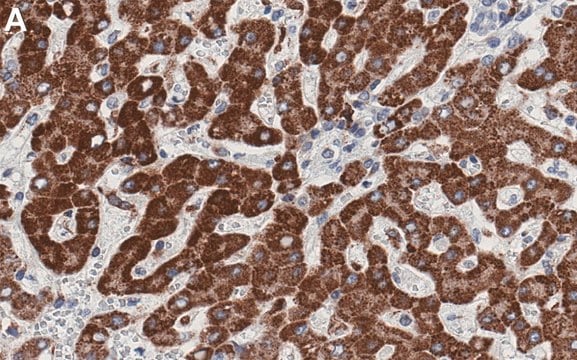
Anti-Cathepsin D, rabbit polyclonal, recognizes the ~50 kDa latent and the ~30 kDa active forms in breast carcinoma cell line. It is validated for ELISA, Western blotting, and immunoelectrophoresis.
Rabbit polyclonal antibody purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation. Recognizes the ~50 kDa latent and the ~30 kDa active forms of cathepsin D.
Recognizes the ~50 kDa latent and the ~30 kDa active forms of cathepsin D in breast carcinoma cell line.
Immunogen
Human
purified human liver cathepsin D
Application
ELISA (≥1:1000)
Immunoelectrophoresis (see comments)
Immunoelectrophoresis (see comments)
Packaging
Please refer to vial label for lot-specific concentration.
Warning
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
Physical form
In PBS.
Reconstitution
Following initial use, aliquot and freeze (-20°C) for long-term storage. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Analysis Note
Positive Control
Human liver tissue
Human liver tissue
Other Notes
Monospecific for cathepsin D as determined by a single arc by immunoelectrophoresis against crude live extract and purified cathepsin D. Variables associated with assay conditions will dictate the proper working dilution.
Legal Information
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Maya M Polovitskaya et al.
American journal of human genetics, 107(6), 1062-1077 (2020-11-21)
Dysfunction of the endolysosomal system is often associated with neurodegenerative disease because postmitotic neurons are particularly reliant on the elimination of intracellular aggregates. Adequate function of endosomes and lysosomes requires finely tuned luminal ion homeostasis and transmembrane ion fluxes. Endolysosomal
Rachel Allison et al.
The Journal of cell biology, 216(5), 1337-1355 (2017-04-09)
Contacts between endosomes and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) promote endosomal tubule fission, but the mechanisms involved and consequences of tubule fission failure are incompletely understood. We found that interaction between the microtubule-severing enzyme spastin and the ESCRT protein IST1 at
Gonzalo A Mardones et al.
Molecular biology of the cell, 18(9), 3486-3501 (2007-06-29)
The sorting of acid hydrolase precursors at the trans-Golgi network (TGN) is mediated by binding to mannose 6-phosphate receptors (MPRs) and subsequent capture of the hydrolase-MPR complexes into clathrin-coated vesicles or transport carriers (TCs) destined for delivery to endosomes. This
M Heinrich et al.
Cell death and differentiation, 11(5), 550-563 (2004-01-24)
Acidic noncaspase proteases-like cathepsins have been introduced as novel mediators of apoptosis. A clear role for these proteases and the acidic endolysosomal compartment in apoptotic signalling is not yet defined. To understand the role and significance of noncaspases in promoting
James R Edgar et al.
Acta neuropathologica communications, 8(1), 165-165 (2020-10-17)
Autosomal dominant mutations in LITAF are responsible for the rare demyelinating peripheral neuropathy, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1C (CMT1C). The LITAF protein is expressed in many human cell types and we have investigated the consequences of two different LITAF mutations in
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service