MAB8003
Anti-Hepatitis E Virus ORF2.1 Antibody, clone 2E2
clone 2E2, Chemicon®, from mouse
Synonym(s):
HEV
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
NACRES:
NA.41
clone:
2E2, monoclonal
application:
ELISA
IF
WB
IF
WB
species reactivity:
human
technique(s):
ELISA: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
western blot: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
western blot: suitable
citations:
8
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
2E2, monoclonal
species reactivity
human
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG1
shipped in
wet ice
Specificity
ORF2.1, encoded region to capsid protein
Immunogen
Epitope: ORF2.1
Application
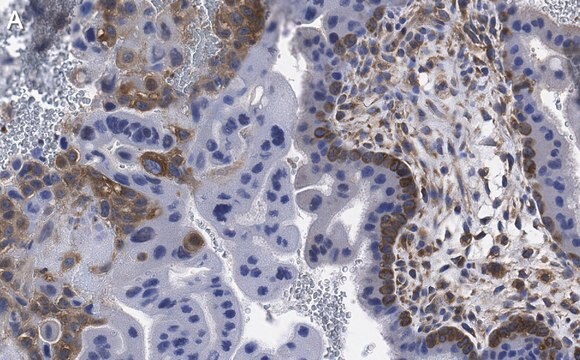
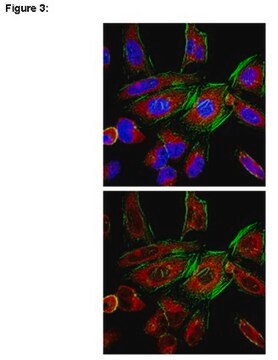
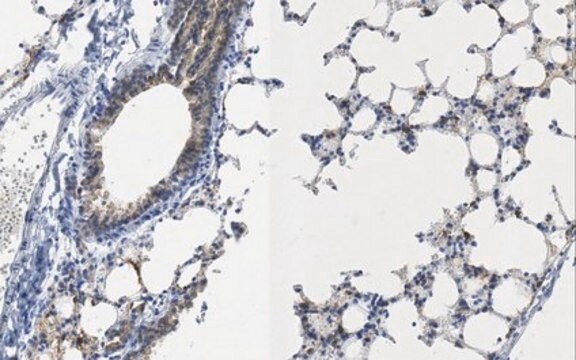
Anti-Hepatitis E Virus ORF2.1 Antibody, clone 2E2 is an antibody against Hepatitis E Virus ORF2.1 for use in WB, ELISA & IF.
ELISA
Immunoblotting
Immunofluorescence
Optimal dilutions must be determined by end user.
Immunoblotting
Immunofluorescence
Optimal dilutions must be determined by end user.
Research Category
Infectious Diseases
Infectious Diseases
Research Sub Category
Infectious Diseases - Viral
Infectious Diseases - Viral
Physical form
Format: Purified
Purified immunoglobulin. Liquid in 0.02M PB with 0.25M NaCl, pH 7.6. Contains 0.1% sodium azide.
Storage and Stability
Store at 2° to 8°C.
Other Notes
Concentration: Please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for the lot-specific concentration.
Legal Information
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Jianwen Situ et al.
Virology, 541, 150-159 (2020-02-15)
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is the main pathogen of hepatitis E infections with multiple extrahepatic replication sites. The presence of HEV RNA in the semen of infertile males suggests HEV replicates in the male genital tract. However, the mechanism is
Weimin Yang et al.
Viruses, 13(10) (2021-10-27)
To evaluate whether uterine injury caused by hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection is responsible for adverse pregnancy outcomes. HEV-infected female BALB/c mice were coupled with healthy male BALB/c mice at 0, 7, 14, 21, and 91 dpi to explore the
Wenhai Yu et al.
BMC infectious diseases, 16, 80-80 (2016-02-18)
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is a major cause of hepatitis in developing countries and poses a threat to public health worldwide. Tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis) is a useful animal model in studies on hepatitis viruses, such as hepatitis B
Shilin Gong et al.
Journal of medical virology, 93(6), 3769-3778 (2020-11-01)
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection has become a global concern with high mortality rates among pregnant women, especially those in their third trimester of pregnancy. Estrogen plays an important role in mediating the body, regulating physiological and pathological processes. Estrogen
Yueping Xia et al.
Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver, 43(2), 317-328 (2022-10-29)
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection causes serious adverse pregnancy outcomes during pregnancy. However, the maternal and fetal damage induced by HEV infection is rarely reported. A BALB/c pregnant mouse model was established to explore the maternal and fetal pathological damage
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service