B6688
BMS 493
≥98% (HPLC), powder, pan-RAR inverse agonist
Synonym(s):
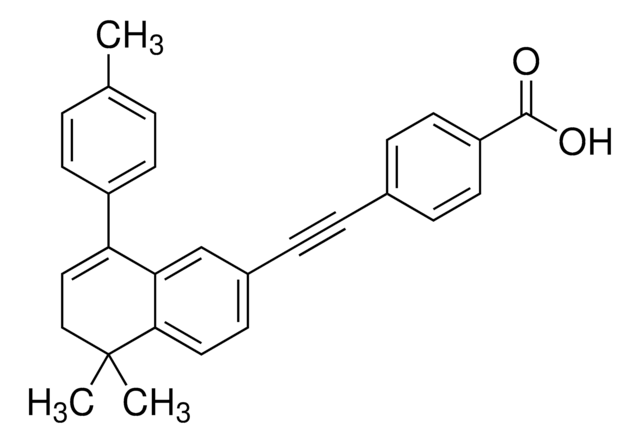
(E)-4-[2-[5,6-Dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-8-(2-phenylethynyl)naphthalen-2-yl]ethen-1-yl]benzoic acid, 4-[(1E)-2-[5,6-Dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-8-(phenylethynyl)-2-naphthalenyl]ethenyl]-benzoic acid, BMS204, 493
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
BMS 493, ≥98% (HPLC)
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
powder
color
light yellow to yellow
solubility
DMSO: ≥20 mg/mL
originator
Bristol-Myers Squibb
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
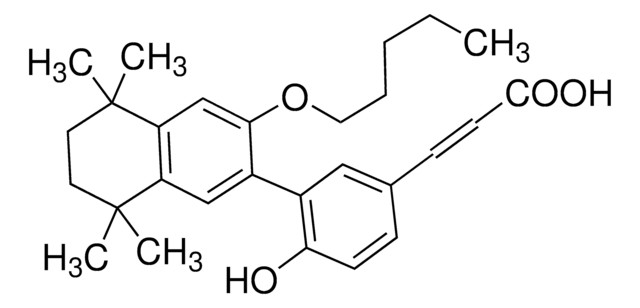
CC1(C)CC=C(C#Cc2ccccc2)c3cc(\C=C\c4ccc(cc4)C(O)=O)ccc13
InChI
1S/C29H24O2/c1-29(2)19-18-24(14-10-21-6-4-3-5-7-21)26-20-23(13-17-27(26)29)9-8-22-11-15-25(16-12-22)28(30)31/h3-9,11-13,15-18,20H,19H2,1-2H3,(H,30,31)/b9-8+
InChI key
YCADIXLLWMXYKW-CMDGGOBGSA-N
General description
Application
- as an inhibitor for the dietary and pharmacologic manipulation of retinoic acid (RA) activity in vivo and in vitro
- for human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) culture and ventricular cardiomyocytes (VCMs) differentiation
- to inhibit retinoic acid (RA) signaling in explants
- as a retinoic acid receptor (RAR) inhibitor for the induction of synaptonemal complex protein 3 (SCP3) and ATP-dependent RNA helicase (DDX4) in primordial germ cells (PGCs)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
We offer many products related to non-steroid nuclear receptors for your research needs.
Cell cycle phases (G1, S, G2, M) regulate cell growth, DNA replication, and division in proliferating cells.
Apoptosis regulation involves multiple pathways and molecules for cellular homeostasis.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service