T4816
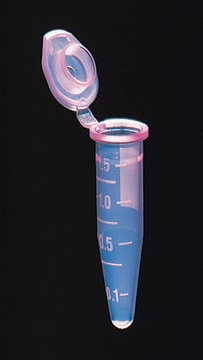
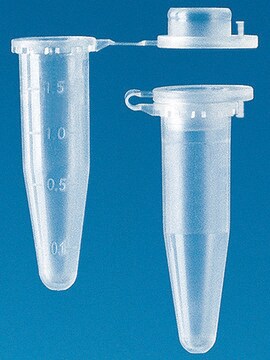
Clear-view™ Snap-Cap microtubes
capacity 1.5 mL, natural, low retention
Synonym(s):
low retention microtube, snap-cap vial
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41121702
NACRES:
NB.22
Recommended Products
material
conical bottom
flat cap
polypropylene
sterility
non-sterile
feature
RNase and DNase free
neck thread Push fit
low retention
packaging
pack of 250 ea
manufacturer/tradename
Excel Scientific MCTS 1.5N
parameter
-20,000 × g max. RCF
technique(s)
PCR: suitable
capacity
1.5 mL
color
natural
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
- Superior clarity for sample viewing
- A consistent, ring-lock seal prevents inadvertent opening
- Angled cap lid makes opening easy without thumb fatigue
- Large flat tops for ease of identification and a pierceable cap
- Large, crisp reference lines and graduation numbers
- Certified RNase/DNase free
Application
Clear-view™ Snap-Cap microtubes have been used in iCLIP (individual-nucleotide resolution UV crosslinking and immunoprecipitation) protocol. They have been used for the preparation of serum samples for MS/MS (mass spectrometry) analysis.
Legal Information
Clear-view is a trademark of Excel Scientific, Inc.
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Individual-nucleotide-resolution UV Cross-linking and Immunoprecipitation (iCLIP) of UPF1.
Zund D and Muhlemann O
Bio-protocol (2014)
Pre-analytical-related variability influencing serum peptide profiles demonstrated in a mass spectrometry-based search for colorectal and prostate cancer biomarkers.
Karczmarski J, et al.
Acta Biochimica Polonica, 60, 417-425 (2013)
Minh Doan et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(35), 21381-21390 (2020-08-26)
Stored red blood cells (RBCs) are needed for life-saving blood transfusions, but they undergo continuous degradation. RBC storage lesions are often assessed by microscopic examination or biochemical and biophysical assays, which are complex, time-consuming, and destructive to fragile cells. Here
Ruben N Pinto et al.
Cytometry. Part A : the journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology, 95(9), 976-984 (2019-07-12)
Deleterious changes, collectively termed as storage lesions, alter the characteristics of red blood cell (RBC) morphology during in vitro storage. Due to gradual loss of cellular membrane, RBCs lose their original biconcave disk shape and begin a process of spherical
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service