408964
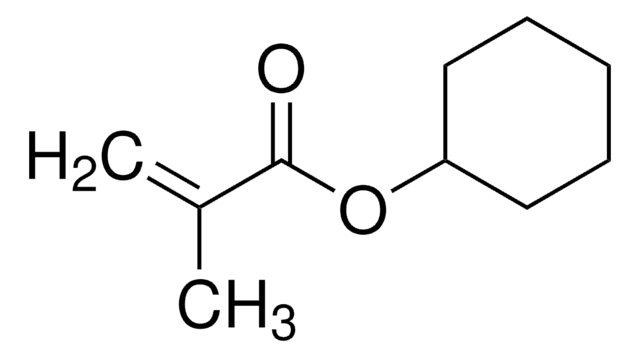
Cyclohexyl methacrylate
≥97%, contains ~60 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Synonym(s):
Methacrylic acid cyclohexyl ester
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥97%
form
liquid
contains
~60 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
refractive index
n20/D 1.458 (lit.)
bp
68-70 °C/4 mmHg (lit.)
density
0.964 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CC(=C)C(=O)OC1CCCCC1
InChI
1S/C10H16O2/c1-8(2)10(11)12-9-6-4-3-5-7-9/h9H,1,3-7H2,2H3
InChI key
OIWOHHBRDFKZNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- As a monomer to prepare poly(cyclohexyl methacrylate) (PCHMA) thin films for high-performance luminescent solar concentrators(LSCs). These LSCs can be used to fabricate high-quantum yield photovoltaic solar cells.
- As a comonomer to prepare photo-patternable quantum dot-acrylate resins for fabricating light-emitting diodes with high color transparency.
- As a monomer to synthesizesuperhydrophobic silica nanoparticle surfaces for various applications such as anti-corrosionsurfaces, drag reduction, and energy conservation.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
181.4 °F
Flash Point(C)
83 °C
Personal Protective Equipment
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
FSL
Group 4: Flammable liquids
Type 3 petroleums
Hazardous rank III
Water insoluble liquid
JAN Code
408964-100ML:
408964-BULK:
408964-250ML:
408964-VAR:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service