751626
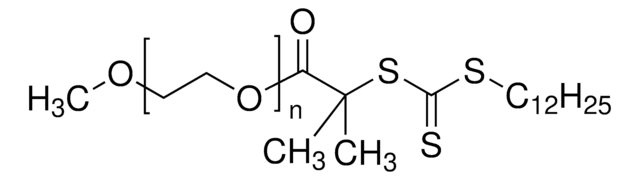
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether (4-cyano-4-pentanoate dodecyl trithiocarbonate)
average Mn 5,400
Synonym(s):
Dodecyl-trithiocarbonate-cyano PEG, PEG-RAFT, Poly(ethylene glycol)methyl ether 4-cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoate
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
solid
Quality Level
mol wt
average Mn 5,400
transition temp
Tm 55-60 °C
PDI
≤1.1
Ω-end
4-cyano-4-pentanoate dodecyl trithiocarbonate
α-end
methoxy
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
751626-5G:
751626-VAR:
751626-1G:
751626-BULK:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization is rapidly moving to the forefront in construction of drug and gene delivery vehicles.
Over the past two decades, the rapid advance of controlled living polymerization (CLP) techniques.
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
Micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization.
Protocols
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
We present an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Polymerization via ATRP procedures demonstrated by Prof. Dave Haddleton's research group at the University of Warwick.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service
![Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether 4-cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoate average Mn 10,000](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/618/250/98532519-ae4b-4fc4-b6f0-fb15f144c8f1/640/98532519-ae4b-4fc4-b6f0-fb15f144c8f1.png)
![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)