765201
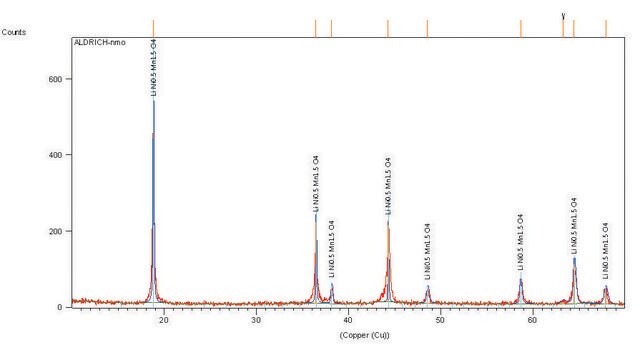
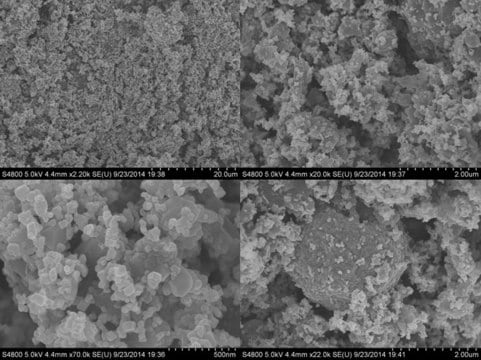
Lithium manganese oxide
spinel, electrode sheet, size 5 in. × 10 in.
Synonym(s):
LMO, Lithium manganese(III,IV) oxide
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
battery grade
description
Nominal Voltage: 4.7 V, Li/Li+
Assay
≥98%
form
sheet
composition
loading, ≥80%
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
extent of labeling
≥80% loading
size
5 in. × 10 in.
thickness
~25 μm
particle size
10-13 μm (typical)
capacity
110 mAh/g
120 mAh/g(nominal at 0.1C)
mp
>1000 °C
application(s)
battery manufacturing
greener alternative category
, Enabling
SMILES string
[Li+].[O-][Mn]=O.O=[Mn]=O
InChI
1S/Li.2Mn.4O/q+1;;;;;;-1
InChI key
VLXXBCXTUVRROQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Application
Other Notes
Operating Condiditons:
- Recommended maximum charge voltage: 5.0 V vs Li/Li+
- Recommended maximum charge current: 3 C
- Recommended cut-off voltage for discharge: 3.5 V vs Li/Li+
- Recommended maximum discharge current: 5 C
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
PRTR
Class I Designated Chemical Substances
ISHL Indicated Name
Substances Subject to be Indicated Names
ISHL Notified Names
Substances Subject to be Notified Names
JAN Code
765201-BULK:
765201-VAR:
765201-1EA:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Professor Qiao's review explores stable microstructures for lithium metal fluoride batteries, advancing energy storage technologies.
Solid oxide fuel cells and electrolyzers show potential for chemical-to-electrical energy conversion, despite early development stages.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service