178501
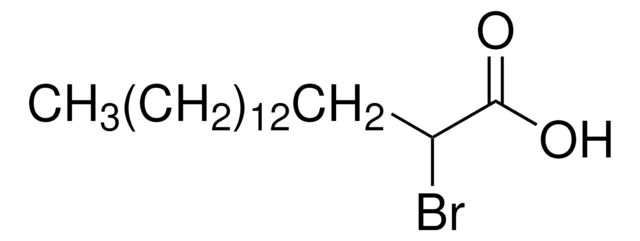
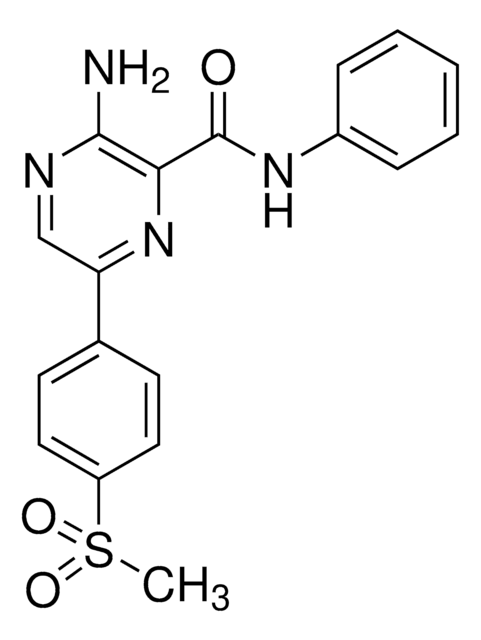
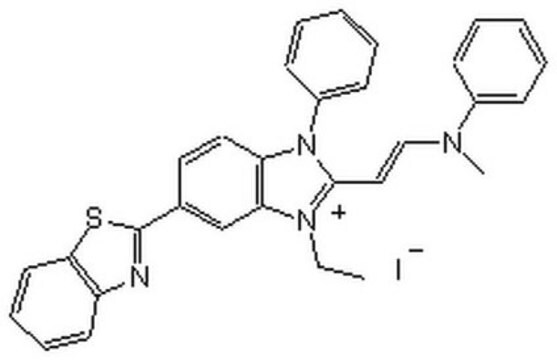
Palmostatin B
≥95% (HPLC), solid, APT1 inhibitor, Calbiochem®
Synonym(s):
APT1 Inhibitor, palmostatin B, APT1 Inhibitor
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
APT1 Inhibitor, palmostatin B, The APT1 Inhibitor, palmostatin B controls the biological activity of APT1.
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
form
solid
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
protect from light
color
off-white
solubility
DMSO: 100 mg/mL
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Packaging
Warning
Other Notes
Dekker, F., et al. 2010. Nat. Chem. Biol.6, 449.
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
178501-MG:
178501-5MG:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service