219557
Cerulenin
from Cephalosporium caerulens, ≥98% (TLC), solid, de novo phospholipid synthesis inhibito, Calbiochem
Synonym(s):
Cerulenin, Cephalosporium caerulens
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Cerulenin, Cephalosporium caerulens, An antifungal antibiotic that inhibits sterol and fatty acid biosynthesis.
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% (TLC)
form
solid
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
protect from light
color
white to off-white
solubility
DMSO: 10 mg/mL
ethanol: 5 mg/mL
acetone: soluble
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
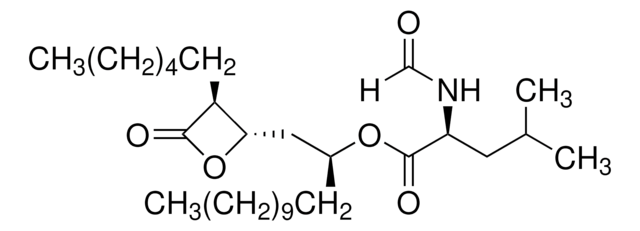
NC(=O)[C@@H]1O[C@@H]1C(=O)CC\C=C\C\C=C\C
InChI
1S/C12H17NO3/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9(14)10-11(16-10)12(13)15/h2-3,5-6,10-11H,4,7-8H2,1H3,(H2,13,15)/b3-2+,6-5+/t10-,11-/m1/s1
InChI key
GVEZIHKRYBHEFX-NQQPLRFYSA-N
General description
Biochem/physiol Actions
sterol & fatty acid biosynthesis
Packaging
Warning
Other Notes
Inokashi, J., et al. 1994. Mol. Gen. Genet. 244, 90.
Schneider, F., et al. 1993. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1152, 243.
Legal Information
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
219557-0MG:
219557-MG:
219557-1GM:
219557-5MG:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service