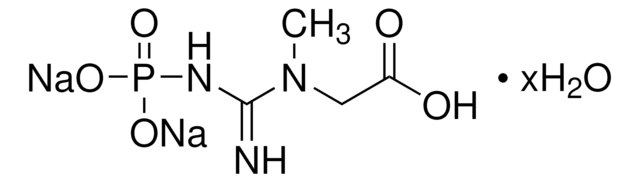
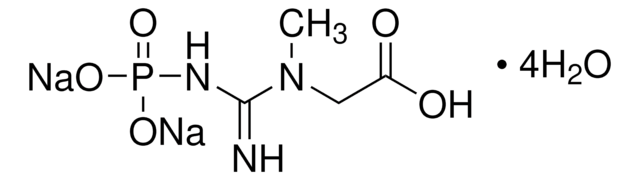
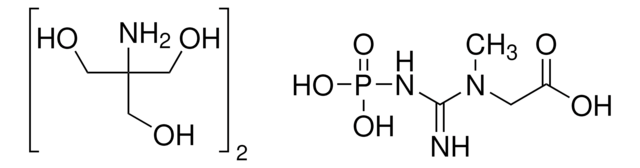
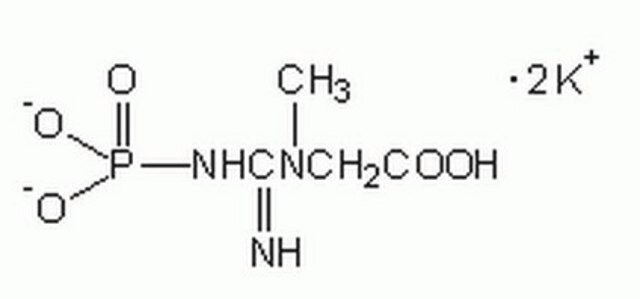
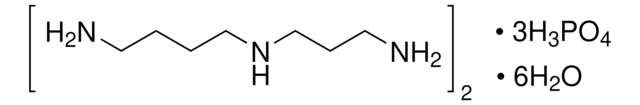
CK-RO
Roche
Creatine Kinase (CK)
from rabbit muscle
Synonym(s):
creatine phosphokinase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit muscle
Quality Level
form
lyophilized
packaging
pkg of 100 mg (10127566001)
pkg of 500 mg (10736988001)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
color
white to light yellow
optimum pH
6.0-7.0(reverse reaction)
9.0(forward reaction)
solubility
water: soluble
suitability
suitable for immunoprecipitation
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
application(s)
life science and biopharma
sample preparation
foreign activity
ATPase <0.001%
HK <0.001%
myokinase <0.001%
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
rabbit ... CKM(100009056)
General description
at 25 °C (800 U/mg lyophilizate at 37 °C) with creatine phosphate and ADP as the substrates, and N-acetyl-L-cysteine as the activator.
Application
Creatine kinase has been used as a component of translation buffer used in in vitro translation assay and as a component of energy regeneration mix.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Creatine kinase (CK) is a guanidino-kinase that catalyzes the reversible phosphorylation of creatine to phosphocreatine at the expense of ATP. It plays crucial roles in rapid regeneration of ATP in cells with high demand for energy. Increased level of CK in human blood indicates diseases of the nervous system and the heart muscle, malignant hypothermia, and certain tumors. Metals such as Mg, Mn and Ca act as cofactors for CK. It also forms a substrate for protein kinase C, an important signaling molecule involved in cell growth. A product of enzymatic reaction of CK, phosphocreatine, is found to prevent HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) replication in macrophages.
Quality
Contaminants: <0.001% ATPase, HK, and myokinase, each
Specifications
Specific activity: Approximately 350U/mg lyophilizate at +25°C (800U/mg lyophilizate at +37°C) with creatine phosphate and ADP as the substrates, and N-acetyl-L-cysteine as activator.
Unit Definition
One unit CK activity (+25 °C) = 2.3 U (+37 °C), creatin-P and ADP as substrates, NAcCys as reactivator.
Physical form
Lyophilizate, stabilized
Preparation Note
Storage conditions (working solution): Working solutions and storage conditions in routine applications:
Dissolve in 0.1 M imidazole buffer; aliquot and store at -15 to -25 °C.
Stable for approximately four weeks at -15 to -25 °C.
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
Dissolve in 0.5% NaHCO3 solution.
Do not freeze. Store protected from light.
Stable for 2 - 3 days, when stored at 2 to 8 °C.
Or
Dissolve in 30 mM glycine buffer, pH 9.0, with 0.2 mM DTT.
Stable for 2 - 3 days, when stored at 2 to 8 °C.
Dissolve in 0.1 M imidazole buffer; aliquot and store at -15 to -25 °C.
Stable for approximately four weeks at -15 to -25 °C.
Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
Dissolve in 0.5% NaHCO3 solution.
Do not freeze. Store protected from light.
Stable for 2 - 3 days, when stored at 2 to 8 °C.
Or
Dissolve in 30 mM glycine buffer, pH 9.0, with 0.2 mM DTT.
Stable for 2 - 3 days, when stored at 2 to 8 °C.
Other Notes
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
does not flash
Flash Point(C)
does not flash
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Irina M Kuznetsova et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1596(1), 138-155 (2002-05-02)
GdmCl-induced unfolding of rabbit muscle creatine kinase, CK, has been studied by a variety of physico-chemical methods including near and far UV CD, SEC, intrinsic fluorescence (intensity, anisotropy and lifetime) as well as intensity and lifetime of bound ANS fluorescence.
Aurélie M Rakotondrafara et al.
Nature protocols, 6(5), 563-571 (2011-04-30)
Much of the regulation of gene expression occurs at the level of protein synthesis. In addition to the canonical translation factors, a multitude of proteins and microRNAs (miRNAs) act as regulatory trans-acting factors. Mechanistic analysis of translational control benefits from
Marta Teperek et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 15(9), 16719-16740 (2014-09-23)
Spermatozoa are more efficient at supporting normal embryonic development than spermatids, their immature, immediate precursors. This suggests that the sperm acquires the ability to support embryonic development during spermiogenesis (spermatid to sperm maturation). Here, using Xenopus laevis as a model
J K Rao et al.
FEBS letters, 439(1-2), 133-137 (1998-12-16)
The crystal structure of rabbit muscle creatine kinase, solved at 2.35 A resolution by X-ray diffraction methods, clearly identified the active site with bound sulfates surrounded by a constellation of arginine residues. The putative binding site of creatine, which is
Marta Teperek et al.
Genome research, 26(8), 1034-1046 (2016-04-02)
For a long time, it has been assumed that the only role of sperm at fertilization is to introduce the male genome into the egg. Recently, ideas have emerged that the epigenetic state of the sperm nucleus could influence transcription
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service