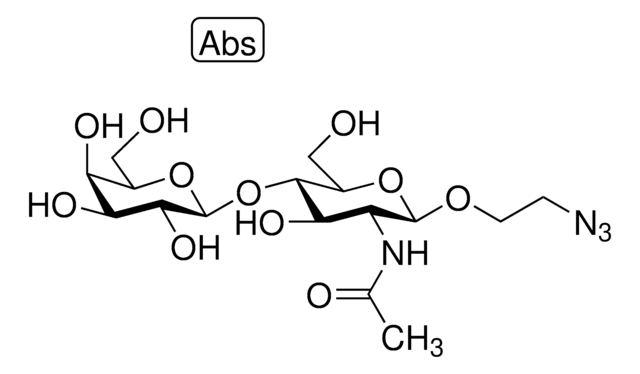
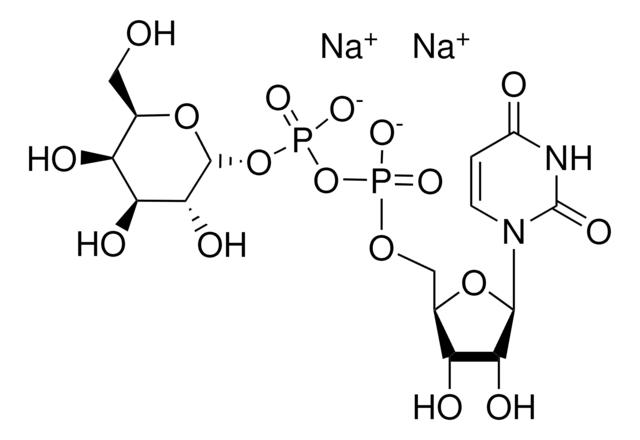
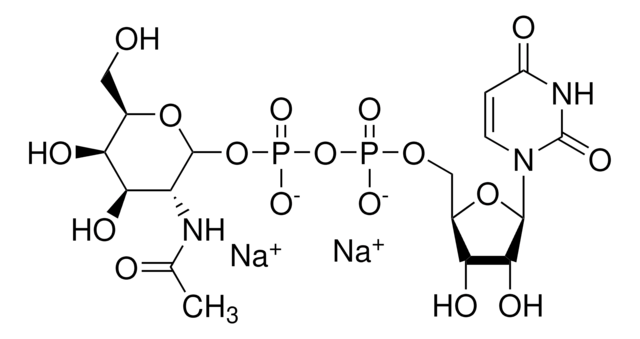
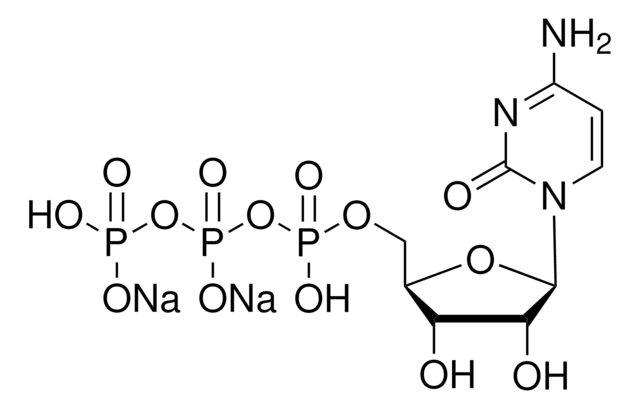
S2076
α-2,6-Sialyltransferase from Photobacterium damsela
recombinant, expressed in E. coli BL21, ≥5 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
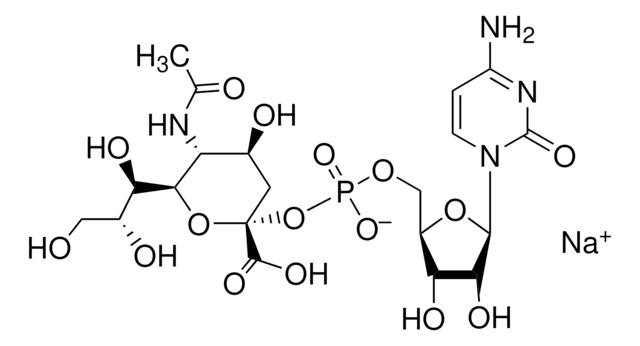
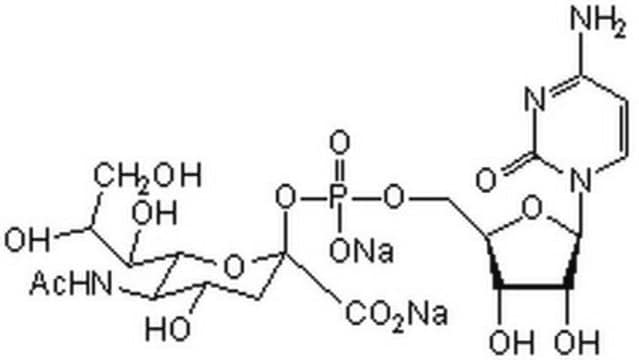
β-Galactoside α-2,6-sialyltransferase, CMP-N-Acetylneuraminate:β-D-galactosyl-1,4-N-acetyl-β-D-glucosamine α-2,6-N-acetylneuraminyltransferase
About This Item
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli BL21
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥5 units/mg protein
mol wt
56.8 kDa
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
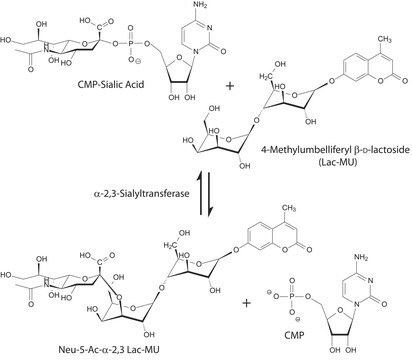
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Physical form
Analysis Note
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
JAN Code
S2076-BULK:
S2076-1UN-PW:
S2076-1UN:
S2076-VAR:
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Explore tools for glycosyltransferase synthesis and modification of glycans, such as glycosyltransferases and nucleotide sugar donors.
Enzymatic glycosyltransferase specificity challenges the one enzyme-one linkage concept.
Understand sialic acid structure, function, signaling, and modifications. Easily find products for sialic acid research.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service