SAE0088
Filipin complex ready made solution
from Streptomyces filipinensis, 5mg/ml in DMSO based solution
Synonym(s):
Filipin solution
About This Item
Recommended Products
Assay
≥90% (HPLC)
form
ready-to-use solution
storage condition
protect from light
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Other Notes
Filipin complex is used in various concentrations depending on the specific protocol used. Dilute 5mg/ml stock solution with appropriate buffer according to the used protocol.
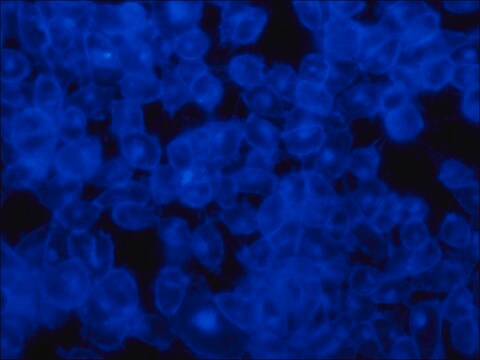
Filipin complex interaction with cholesterol alters the absorption and fluorescence spectra, for visualization with a fluorescence microscope use excitation at 340-380 nm and emission at 385-470 nm (Filipin fluorescent staining photo-bleaches very rapidly, thus the sample should be analyzed immediately).
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
188.6 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
87 °C - closed cup
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
FSL
Group 4: Flammable liquids
Type 3 petroleums
Hazardous rank III
Water insoluble liquid
JAN Code
SAE0088-1ML:
SAE0088-VAR:
SAE0088-BULK:
SAE0088-1ML-PW:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service