SMB00173
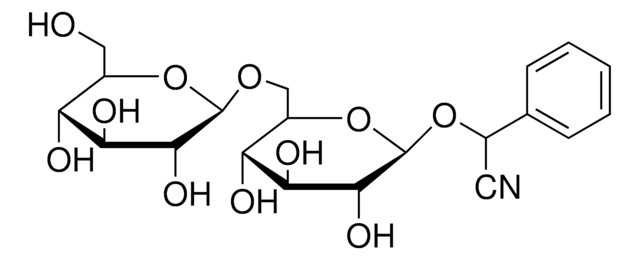
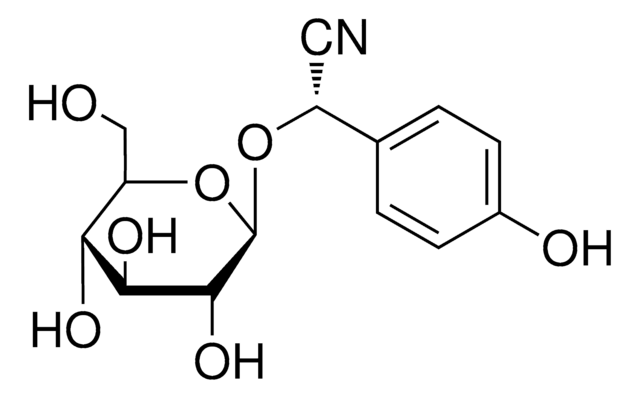
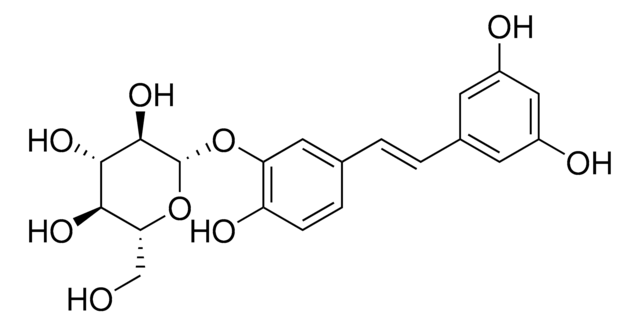
Prunasin
≥90% (LC/MS-ELSD)
Synonym(s):
D-Mandelonitrile β-D-glucoside
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥90% (LC/MS-ELSD)
form
solid
application(s)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
OCC1OC(OC(C#N)c2ccccc2)C(O)C(O)C1O
InChI
1S/C14H17NO6/c15-6-9(8-4-2-1-3-5-8)20-14-13(19)12(18)11(17)10(7-16)21-14/h1-5,9-14,16-19H,7H2
InChI key
ZKSZEJFBGODIJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Repr. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
PDSCL
Deleterious substance
JAN Code
SMB00173-BULK:
SMB00173-1MG:4548173340647
SMB00173-VAR:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service