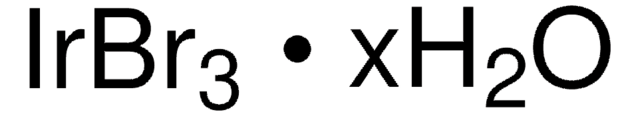206245
Iridium(III) chloride hydrate
reagent grade
Synonym(s):
IrCl3, Iridium trichloride hydrate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
IrCl3 · xH2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
298.58 (anhydrous basis)
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12161600
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
grade
reagent grade
Quality Level
form
solid
reaction suitability
core: iridium
reagent type: catalyst
density
5.3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[H]O[H].Cl[Ir](Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/3ClH.Ir.H2O/h3*1H;;1H2/q;;;+3;/p-3
InChI key
MJRFDVWKTFJAPF-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Iridium(III) chloride hydrate is an inorganic compound used as a catalyst as well as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is used as the source of iridium in the preparation of iridium nanocatalysts.
Application
Iridium(III) chloride hydrate can be used as a precursor in the preparation of:
- Iridium-incorporated cobalt nanofibers.
- Carbon-supported iridium catalyst for the hydrodeoxygenation of hydroxymethylfurfural.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
?Naked? iridium (IV) oxide nanoparticles as expedient and robust catalysts for hydrogenation of nitrogen heterocycles: remarkable vicinal substitution effect and recyclability
Ji YG, et al.
Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 359, 933-940 (2017)
Maximilian Moser et al.
Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 53(33), 8628-8633 (2014-06-04)
Rutile TiO2 is a heavily investigated oxide with, to date, scarce applications in industrial catalysis. The inactivity of this material in oxidations has been related to its inability to dissociate molecular oxygen. Herein we show how rutile catalyzes the oxidation
Comparison of HMF hydrodeoxygenation over different metal catalysts in a continuous flow reactor
Applied Catalysis A: General, 508, 86-93 (2015)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service