All Photos(2)
About This Item
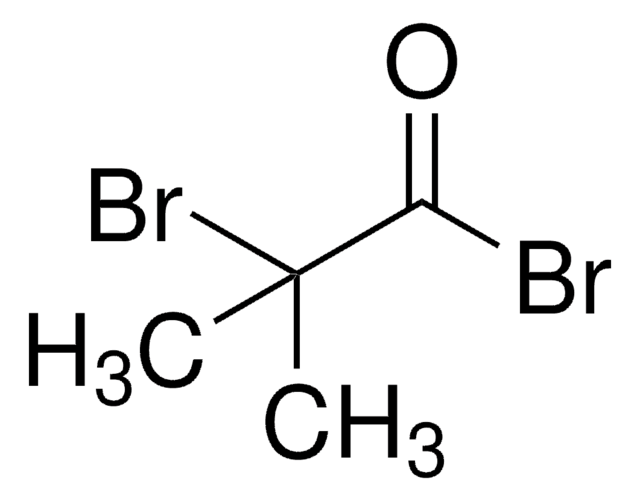
Linear Formula:
H2C=C(CH3)CONHCH(CH3)2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
127.18
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12162002
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Assay
97%
mp
89-91 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CC(C)NC(=O)C(C)=C
InChI
1S/C7H13NO/c1-5(2)7(9)8-6(3)4/h6H,1H2,2-4H3,(H,8,9)
InChI key
YQIGLEFUZMIVHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Adriana M Mihut et al.
Science advances, 3(9), e1700321-e1700321 (2017-09-21)
We have seen a considerable effort in colloid sciences to copy Nature's successful strategies to fabricate complex functional structures through self-assembly. This includes attempts to design colloidal building blocks and their intermolecular interactions, such as creating the colloidal analogs of
S Brosel-Oliu et al.
Lab on a chip, 19(8), 1436-1447 (2019-03-19)
The presence of antimicrobial contaminants like antibiotics in the environment is a major concern because they promote the emergence and the spread of multidrug resistant bacteria. Since the conventional systems for the determination of bacterial susceptibility to antibiotics rely on
Viktor Sabadasch et al.
Soft matter, 16(23), 5422-5430 (2020-06-04)
Responsive core-shell microgels are promising systems for a stabilization of Pd nanoparticles and control of their catalytic activity. Here, poly-N-n-propylacrylamide (PNNPAM) was copolymerized with methacrylic acid to yield microgel core particles, which were subsequently coated with an additional, acid-free poly-N-isopropylmethacrylamide
Timo Brändel et al.
Polymers, 11(8) (2019-08-03)
The present study focuses on the development of multiresponsive core-shell microgels and the manipulation of their swelling properties by copolymerization of different acrylamides-especially N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), N-isopropylmethacrylamide (NIPMAM), and NNPAM-and acrylic acid. We use atomic force microscopy for the dry-state characterization
Sonal Deshpande et al.
Soft matter, 14(20), 4169-4177 (2018-04-25)
RNAi is emerging as a promising technology for treatment of various diseases due to its ability to silence specific target genes. To date, a number of nanoparticle based formulations have been reported for the delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service