671576
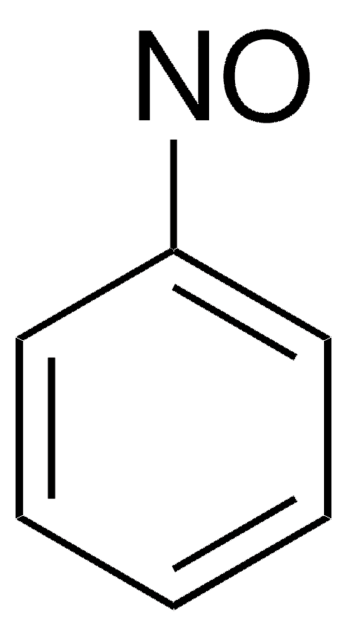
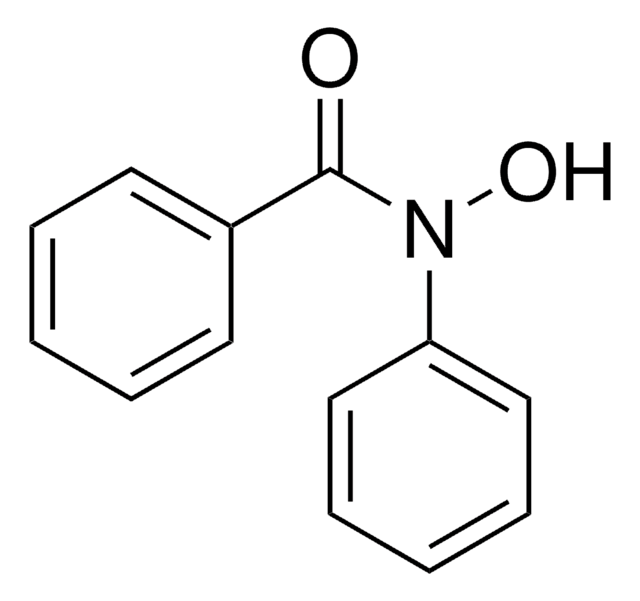
N-Phenylhydroxylamine
≥95.0%
Synonym(s):
N-Hydroxyaniline, N-Hydroxybenzenamine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C6H7NO
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
109.13
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95.0%
form
solid
mp
80-84 °C
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
ONc1ccccc1
InChI
1S/C6H7NO/c8-7-6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h1-5,7-8H
InChI key
CKRZKMFTZCFYGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
Application
N-Phenylhydroxylamine can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of:
- 2-alkylindoles by treating with aliphatic terminal alkynes using gold catalyst via sequential 3,3-rearrangements and cyclodehydrations.
- Isoxazolidines by reacting with aldehydes and α, β-unsaturated aldehydes via a three-component one-pot catalytic reaction.
- Tetrahydro-1,2-oxazines by treating with an aldehyde and cyclopropane via homo 3+2 dipolar cycloaddition reaction.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Z He et al.
European journal of biochemistry, 267(4), 1110-1116 (2000-02-15)
Hydroxylaminobenzene mutase is the enzyme that converts intermediates formed during initial steps in the degradation of nitrobenzene to a novel ring-fission lower pathway in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes JS45. The mutase catalyzes a rearrangement of hydroxylaminobenzene to 2-aminophenol. The mechanism of the
Magnesium iodide promoted reactions of nitrones with cyclopropanes: a synthesis of tetrahydro-1, 2-oxazines.
Ganton M D and Kerr M A
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 69(24), 8554-8557 (2004)
Vance G Nielsen et al.
Blood coagulation & fibrinolysis : an international journal in haemostasis and thrombosis, 22(8), 657-661 (2011-08-09)
Cigarette smoking is associated with plasmatic hypercoagulability, and carbon monoxide has been demonstrated to enhance coagulation by binding to a fibrinogen-bound heme. Our objective was to design and test a redox-based method to detect carboxyhemefibrinogen. Normal, pooled, citrated plasma was
Lloyd J Nadeau et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 69(5), 2786-2793 (2003-05-07)
Hydroxylamino aromatic compounds are converted to either the corresponding aminophenols or protocatechuate during the bacterial degradation of nitroaromatic compounds. The origin of the hydroxyl group of the products could be the substrate itself (intramolecular transfer mechanism) or the solvent water
C C Somerville et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 177(13), 3837-3842 (1995-07-01)
Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes JS45 grows on nitrobenzene as a sole source of carbon, nitrogen, and energy. The catabolic pathway involves reduction to hydroxylaminobenzene followed by rearrangement to o-amino-phenol and ring fission (S. F. Nishino and J. C. Spain, Appl. Environ. Microbiol.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service