910007
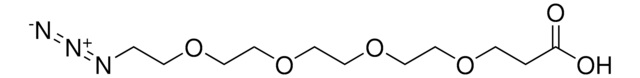
20-Azido-3,6,9,12,15,18-hexaoxaicosanoic acid
95%
Synonym(s):
Azido-PEG6-CH2CO2H, Azido-PEG6-acid, N3-PEG6-CH2COOH
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C14H27N3O8
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
365.38
UNSPSC Code:
12352106
Recommended Products
Assay
95%
form
(Liquid or Semi-Solid or Paste or Solid)
reaction suitability
reaction type: click chemistry
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
functional group
azide
carboxylic acid
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
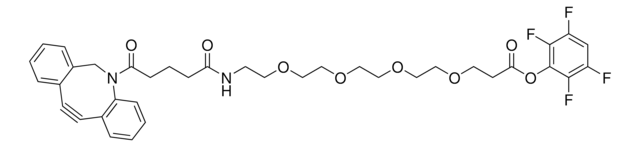
OC(COCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCN=[N+]=[N-])=O
Application
This heterobifunctional, PEGylated crosslinker 20-Azido-3,6,9,12,15,18-hexaoxaicosanoic acid features a carboxyl group at one end and azide at the other. The hydrophillic PEG linker facilitates solubility in biological applications. This azido-PEG6-acid linker can be used for bioconjugation or as a building block for synthesis of small molecules, conjugates of small molecules and/or biomolecules, or other tool compounds for chemical biology and medicinal chemistry that require ligation. Examples of applications include its synthetic incorporation into antibody-drug conjugates or proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTAC® molecules) for targeted protein degradation.
Legal Information
PROTAC is a registered trademark of Arvinas Operations, Inc., and is used under license
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Towards potential nanoparticle contrast agents: Synthesis of new functionalized PEG bisphosphonates.
Souad Kachbi-Khelfallah et al.
Beilstein journal of organic chemistry, 12, 1366-1371 (2016-08-26)
The use of nanotechnologies for biomedical applications took a real development during these last years. To allow an effective targeting for biomedical imaging applications, the adsorption of plasmatic proteins on the surface of nanoparticles must be prevented to reduce the
Joel Hwang et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 50(24), 3159-3162 (2014-01-30)
Oligo(ethylene glycol)-linked light fluorous tags have been found to be optimal for conjugating to glycans for both high-yield enzymatic glycosylation reactions using one-pot multienzyme (OPME) systems and quick product purification using fluorous solid-phase extraction (FSPE) cartridges. The combination of OPME
Ryota Sato et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 139(48), 17397-17404 (2017-11-10)
Single-molecule imaging (SMI) has been widely utilized to investigate biomolecular dynamics and protein-protein interactions in living cells. However, multicolor SMI of intracellular proteins is challenging because of high background signals and other limitations of current fluorescence labeling approaches. To achieve
Yong Ma et al.
Bioconjugate chemistry, 21(11), 1994-1999 (2010-10-14)
A surface-bound cytomimetic assembly based on chemically selective and biocompatible immobilization and further modification of intact liposome is described. Liposomes carrying PEG-triphenylphosphine were chemoselectively immobilized onto azide-modified glass slides through Staudinger ligation, followed by modification with azide-modified lactose as a
Mingcheng Qian et al.
ChemMedChem, 13(9), 944-956 (2018-02-17)
Currently, there is mounting evidence that intermolecular receptor-receptor interactions may result in altered receptor recognition, pharmacology and signaling. Heterobivalent ligands have been proven useful as molecular probes for confirming and targeting heteromeric receptors. This report describes the design and synthesis
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service