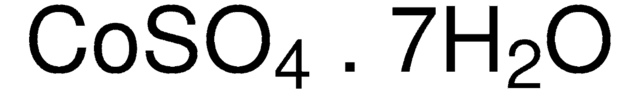939331
Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate

≥99.99% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Nickelous Sulfate, Hexahydrate, Battery grade nickel sulfate, Nickel monosulfate hexahydrate, Nickel sulphate hexahydrate
About This Item
Recommended Products
type
(High purity Salts)
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.99% trace metals basis
98-102% (EDTA, complexometric)
form
powder or crystals
impurities
≤1000 ppm trace metals basis
color
faint blue to dark blue-green
pH
4.3-4.7 (20 °C, 100 g/L in water)
solubility
water: soluble
density
2.07 g/cm3 at 20 °C
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤20 ppm
cation traces
Al: <50 ppm
Ca: <50 ppm
Co: <50 ppm
Cu: <50 ppm
Fe: <50 ppm
K: <50 ppm
Mg: <50 ppm
Na: <50 ppm
Pb: <50 ppm
Zn: <50 ppm
SMILES string
[Ni+2].[S](=O)(=O)([O-])[O-].O.O.O.O.O.O
InChI
1S/Ni.H2O4S.6H2O/c;1-5(2,3)4;;;;;;/h;(H2,1,2,3,4);6*1H2/q+2;;;;;;;/p-2
InChI key
RRIWRJBSCGCBID-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Therefore, Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate has been widely used as a key component for the synthesis of Cathode for Lithium-ion batteries. - Spherical NCM 622 and Li[Ni0.9Co0.05Mn0.05]O2 (NCM 900505) were synthesized via a co-precipitation method using Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate. In order to achieve the desired energy density, it is necessary to maximize both the nickel content in the cathode and the cutoff voltage. [] - to synthesis single-crystal, Ni-rich NCM and polycrystalline NCM cathodes with various Ni content by coprecipitation method . These Ni-rich layered cathodes like NCM, NCA, and NCMA ([Ni1–x–yCox(Mn and/or Al)y]O2) are the top choices for powering upcoming electric vehicles. It is found that polycrystalline NCM cathodes are prone to intergranular microcracking during cycling, single crystal NCM cathodes demonstrate resilience against mechanical fracture, even under highly charged conditions or repeated cycles. Due to limited lithium-ion diffusion pathways, the electrochemical performance of single crystal -NCM cathodes, particularly in terms of capacity and cycling stability, is lower compared to that of polycrystalline-NCM cathodes. The difference in the electrochemical performance of single crystal -NCM and polycrystalline-NCM cathodes grows as the Ni fraction increases. In addition, Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate is widely used for electroplating for producing metallic coatings. Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate can also be used as a catalyst in: -Pt50Ni50 catalysts supported on MCM-41 were produced using wet co-impregnation. These catalysts were then employed for hydrogenation reactions of benzene in gas phase. The morphology of the metal phase within the catalysts has a notable impact on the conversion of benzene to cyclohexane. Factors like reduction temperature, NaBH4 concentration, and reduction medium influence the particle morphology. []
Features and Benefits
- Water soluble
- Medium purity (99.9%)
- Low trace metals in ppm level
- Cost effective Suitable for battery applications
- Recycled catalyst
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Carc. 1A Inhalation - Muta. 2 - Repr. 1B - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Target Organs
Respiratory Tract
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service