C15605
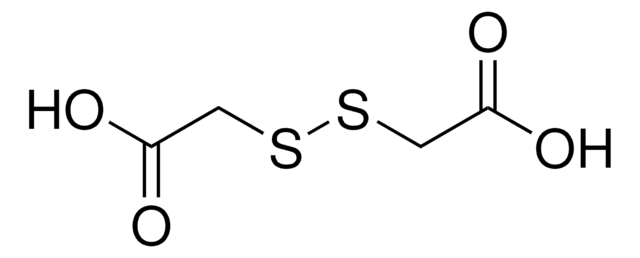
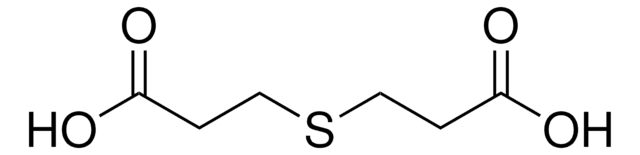
4,4′-Dithiodibutyric acid
95%
Synonym(s):
3-Carboxypropyl disulfide, Di(4-carboxybutyl) disulfide
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
[-S(CH2)3CO2H]2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
238.32
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
95%
form
solid
mp
108-110 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
OC(=O)CCCSSCCCC(O)=O
InChI
1S/C8H14O4S2/c9-7(10)3-1-5-13-14-6-2-4-8(11)12/h1-6H2,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)
InChI key
YYSCJLLOWOUSHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
4,4′-Dithiodibutyric acid is an organic sulfur compound, primarily used as a cross-linking agent in the synthesis of polymers and materials.
Application
4,4′-Dithiodibutyric acid can be used as:
- A precursor to produce novel polythioester (PTE).
- A reactant in the production of chemically crosslinked epoxidized natural rubber.
- An alternative monolayer for protein chips.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
A Silvestri et al.
Nanoscale, 9(38), 14730-14739 (2017-09-28)
In the biomedical applications of nanoparticles (NPs), the proper choice of surface chemistry is a crucial aspect in their design. The nature of the coating can heavily impact the interaction of NPs with biomolecules, affect the state of aggregation, and
Development and characterization of 4, 4?-dithiodibutyric acid as a monolayer for protein chip
Jang, et al.
Sensors and Materials, 18, 367-380 (2006)
Genome and proteome analysis of Rhodococcus erythropolis MI2: Elucidation of the 4, 4-dithiodibutyric acid catabolism
Khairy, et al.
PLoS ONE, 11, e0167539-e0167539 (2016)
Biodegradation of the organic disulfide 4, 4?-dithiodibutyric acid by Rhodococcus spp
Khairy, et al.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81, 8294-8306 (2015)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service