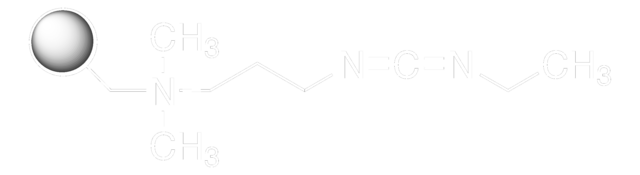
E7750
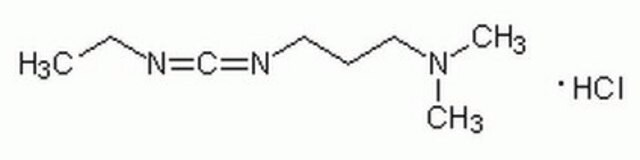
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
commercial grade, powder
Synonym(s):
N-Ethyl-N′-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, EDAC, EDC, EDC hydrochloride, WSC hydrochloride
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
grade
commercial grade
form
powder
technique(s)
Northern blotting: suitable
bioconjugation: suitable
color
white to off-white
mp
110-115 °C (lit.)
solubility
H2O: ≤100 mg/mL
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C
InChI
1S/C8H17N3.ClH/c1-4-9-8-10-6-5-7-11(2)3;/h4-7H2,1-3H3;1H
InChI key
FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
The versatility of EDC HCl further manifests in its capacity to modify nucleic acids, allowing for the labeling of DNA and RNA through their 5′ phosphate groups. This functionality enhances the visualization, tracking, and analysis of these crucial molecules, contributing significantly to the progression of nucleic acid research. Moreover, EDC HCl serves as a vital biomolecule bridge, acting as a crosslinker that connects amine-reactive NHS-esters of biomolecules to carboxyl groups. This technique is particularly valuable in protein conjugation, enabling the creation of hybrid molecules with novel properties and functions. The underlying mechanism of EDC HCl involves its reaction with a carboxyl group, forming an unstable intermediate that actively seeks an amine partner. The delicate balance of this reaction emphasizes the need for optimizing conditions to ensure efficient conjugation. The assistance of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) further enhances EDC HCl′s capabilities by stabilizing the intermediate and enabling two-step conjugation procedures, offering greater flexibility and control, especially when dealing with complex biomolecules.
Application
- N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride has been used for the formation of FND (fluorescent nanodiamonds)-transferrin bioconjugates.
- It has been used for crosslinking polyethylenimine to gold particles.
- It has been used as a carbodiimide linkage agent for coating of carboxylated polystyrene beads with biotinylated BSA (bovine serum albumin).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Other Notes
also commonly purchased with this product
comparable product
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Target Organs
Stomach,large intestine,lymph node
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Click chemistry, and the copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) in particular, is a powerful new synthetic tool in polymer chemistry and material science.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service



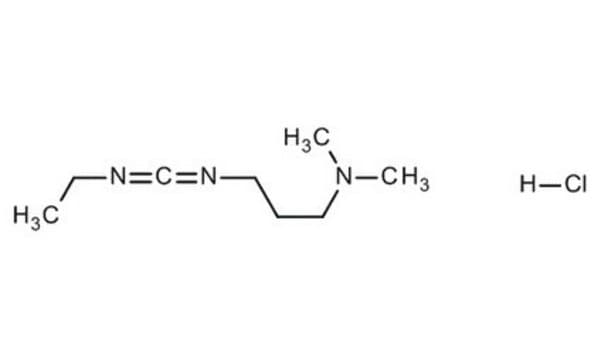



![1-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylcarbodiimide methiodide](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/414/134/4eb9c126-d7f9-4e12-9e3a-95cb077824fd/640/4eb9c126-d7f9-4e12-9e3a-95cb077824fd.png)