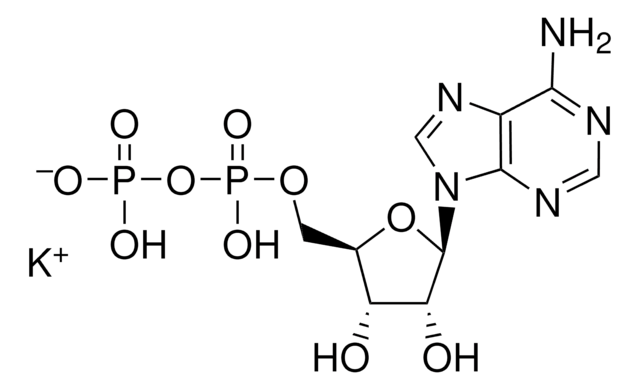
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine heart
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (GE)
form
powder or crystals
mol wt
Mr ~13000
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
impurities
≤5% cytochrome c reduced
solubility
H2O: 10 mg/mL, clear, dark red-brown
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
cow ... CYCS(510767)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Preparation Note
Prepared by a procedure using TCA.
Other Notes
Sales restrictions may apply.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Why is the reduction of NO in cytochrome c dependent nitric oxide reductase (cNOR) not electrogenic?
Margareta R A Blomberg et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1827(7), 826-833 (2013-04-27)
The membrane-bound enzyme cNOR (cytochrome c dependent nitric oxide reductase) catalyzes the reduction of NO in a non-electrogenic process. This is in contrast to the reduction of O2 in cytochrome c oxidase (CcO), the other member of the heme-copper oxidase
Alexander N Volkov et al.
Biochemistry, 52(13), 2165-2175 (2013-03-23)
Here we present the preparation, biophysical characterization, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy study of yeast cytochrome c peroxidase (CcP) constructs with enhanced solubility. Using a high-yield Escherichia coli expression system, we routinely produced uniformly labeled [(2)H,(13)C,(15)N]CcP samples with high
Shujun Yuan et al.
Biochemistry, 52(13), 2319-2327 (2013-03-26)
Apoptosome assembly is highly regulated in the intrinsic cell death pathway. To better understand this step, we created an improved model of the human apoptosome using a crystal structure of full length Apaf-1 and a single particle, electron density map
Gongquan Li et al.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 434(4), 809-814 (2013-04-25)
Small-molecule Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor Navitoclax represents a promising cancer therapeutic since preclinical and clinical studies with Navitoclax have demonstrated strong anticancer activity in several types of cancers. However, because Navitoclax has a low binding affinity to Mcl-1, anticancer activity by Navitoclax
Charles M Keyari et al.
Journal of medicinal chemistry, 56(10), 3806-3819 (2013-04-12)
A series of 7-amino- and 7-acetamidoquinoline-5,8-diones with aryl substituents at the 2-position were synthesized, characterized, and evaluated as potential NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1) -directed antitumor agents. The synthesis of lavendamycin analogues is illustrated. Metabolism studies demonstrated that 7-amino analogues were generally
Chromatograms
application for HPLCapplication for HPLCapplication for HPLCOur team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service