All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
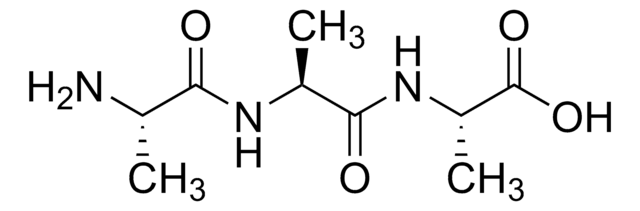
C6H12N2O3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
160.17
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
product name
D-Ala-D-Ala,
Assay
≥99%
Quality Level
form
powder
color
white to off-white
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
C[C@@H](N)C(=O)N[C@H](C)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C6H12N2O3/c1-3(7)5(9)8-4(2)6(10)11/h3-4H,7H2,1-2H3,(H,8,9)(H,10,11)/t3-,4-/m1/s1
InChI key
DEFJQIDDEAULHB-QWWZWVQMSA-N
Application
- Binding Mode-Based Physicochemical Screening Method Using d-Ala-d-Ala Silica Gel and Chemical Modification Approach to Facilitate Discovery of New Macrolactams, Banglactams A and B, from Nonomuraea bangladeshensis K18-0086.: Describes a novel screening method employing D-Ala-D-Ala silica gel to discover new macrolactams with potential antibacterial properties. This technique aids in identifying compounds that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis (Kimishima et al., 2024).
Biochem/physiol Actions
D-Ala-D-Ala is found in the stem termini of peptidoglycan side-chain pentapeptide found in the cell walls of gram positive bacteria. The D-ala-d-ala stem termini is the site of interaction of glycopeptide antibiotics such as vancomycin and teicoplanin. D-ala-D-ala is a substrate used to study kinetics of UDPMurNAc-tripeptide D-alanyl-D-alanine-adding (ligase) enzyme.
D-Ala-D-Ala, a terminus moiety of bacterial peptidoglycans, is used for affinity chromatography and binding mechanism studies of antibiotics such as teicoplanin, ristocetin, vancomycin.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Gareth A Prosser et al.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 60(10), 6091-6099 (2016-08-03)
The increasing global prevalence of drug resistance among many leading human pathogens necessitates both the development of antibiotics with novel mechanisms of action and a better understanding of the physiological activities of preexisting clinically effective drugs. Inhibition of peptidoglycan (PG)
I Tytgat et al.
Current medicinal chemistry, 16(20), 2566-2580 (2009-07-16)
DD-ligases catalyze the synthesis of the D-Ala-D-Ala and D-Ala-D-Ser dipeptides or the D Ala-D-Lac depsipeptide in an early step of peptidoglycan synthesis. Their function is essential for bacterial growth and specific to bacteria, making them attractive targets for the development
Maulik N Thaker et al.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 59(3), 1405-1410 (2014-12-17)
Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) are notorious clinical pathogens restricting the use of glycopeptide antibiotics in the clinic setting. Routine surveillance to detect VRE isolated from patients relies on PCR bioassays and chromogenic agar-based test methods. In recent years, we and others
Yoshiaki Kitamura et al.
Acta crystallographica. Section D, Biological crystallography, 65(Pt 10), 1098-1106 (2009-09-23)
D-Alanine-D-alanine ligase (Ddl) is one of the key enzymes in peptidoglycan biosynthesis and is an important target for drug discovery. The enzyme catalyzes the condensation of two D-Ala molecules using ATP to produce D-Ala-D-Ala, which is the terminal peptide of
Nayeong Kim et al.
BMC microbiology, 21(1), 27-27 (2021-01-20)
Zinc uptake-regulator (Zur)-regulated lipoprotein A (ZrlA) plays a role in bacterial fitness and overcoming antimicrobial exposure in Acinetobacter baumannii. This study further characterized the zrlA gene and its encoded protein and investigated the roles of the zrlA gene in bacterial
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service