M5319
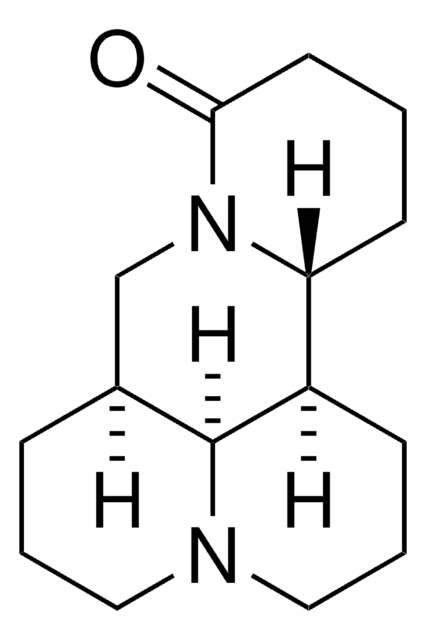
Matrine
Synonym(s):
Matridin-15-one, Sophocarpidine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C15H24N2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
248.36
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
Quality Level
application(s)
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O=C1CCCC2C3CCCN4CCCC(CN12)C34
InChI
1S/C15H24N2O/c18-14-7-1-6-13-12-5-3-9-16-8-2-4-11(15(12)16)10-17(13)14/h11-13,15H,1-10H2/t11-,12+,13+,15-/m0/s1
InChI key
ZSBXGIUJOOQZMP-JLNYLFASSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Matrine (MT) or Sophocarpidine is a naturally occurring bioactive compound, extracted from traditional Chinese herbs like Sophora flavescens and Radix Sophorae tonkinensis.
Application
Matrine has been used:
- to study its antioxidant and protective effect on doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiotoxicity in mice model and H9C2 cells
- as a chemotherapeutic agent to test its inhibitory effect on the growth of human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells, and ovarian cancer cells
- to study its effect on mitochondrial fission and its anti-tumor functionality in HepG2 cells
- as a necroptosis inducer in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cell lines
Biochem/physiol Actions
Matrine is a potent therapeutic agent with various pharmacological like anti-cancer, anti-bacterial, anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory properties. It is a macropinocytosis inducer and decreases the cellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) level. Matrine may also serve as an effective sedative agent. It serves as an anti-inflammatory agent in 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced intestinal inflammation in mice. It functions to reverse the Warburg effect and suppress the growth of human colon cancer cells.
Matrine is an alkaloid that is one of the major components in the root of the saphoro plant. Matrine has been studied for possible antiviral efficacy against hepatitis B and C, as well as impact against some skin diseases and forms of cancer.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Xin Liang et al.
Oncology reports, 45(5) (2021-04-01)
Ovarian cancer displays the highest mortality rate among all types of gynecological cancer worldwide. The survival of patients with ovarian cancer remains poor due to poor responses to anticancer treatments. The present study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects and
Xiao-Yan Liu et al.
International journal of dermatology, 47(5), 448-456 (2008-04-17)
Matrine is a traditional Chinese medicine with significant inhibitory activity against malignant tumors. Its effects on the invasiveness and metastasis of malignant tumors have rarely been reported. To investigate whether matrine can inhibit the metastasis-related activities of the human malignant
Arsenic trioxide-induced hERG K(+) channel deficiency can be rescued by matrine and oxymatrine through up-regulating transcription factor Sp1 expression.
Zhang Y, Dong Z, Jin L, et al.
Biochemical Pharmacology (2012)
Peiyuan Li et al.
Frontiers in physiology, 10, 28-28 (2019-02-26)
This study mainly investigated the effect of matrine on TNBS-induced intestinal inflammation in mice. TNBS treatment caused colonic injury and gut inflammation. Matrine (1, 5, and 10 mg/kg) treatment alleviated colonic injury and gut inflammation via reducing bleeding and diarrhea
Wenjing Zhou et al.
Cancer medicine, 7(9), 4729-4743 (2018-08-07)
Matrine, a traditional Chinese medicine, has recently been shown to have antitumor properties in diverse cancer cells. Here, we explored the effect of matrine on human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells. Glioblastoma multiforme cell lines were treated with matrine to assess
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service