M6435
Methionine Aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus
≥93% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Quality Level
Assay
≥93% (SDS-PAGE)
form
solution
specific activity
0.5 units/mg protein
mol wt
37 kDa by SDS-PAGE
UniProt accession no.
foreign activity
Other proteases, none detected
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638 ... PF0541(1468383)
General description
Methionine aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus is a 32 kDa thermostable enzyme. It belongs to type 2a class of methionine aminopeptidase. Methionine aminopeptidase maintains protein homeostasis and coordinates posttranslational modification of proteins in eukaryotes.
X-ray crystallography of the structure of methionine aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus or PfMAP was performed at a resolution of 1.75A and showed that the protein consists of a catalytic domain containing two cobalt ions in the active site and a unique insertion domain which is specific to the prokaryotic form of the protein.
Application
Methionine Aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus has been used in a study to analyze the binding of Co(II)-specific inhibitors to the methionyl aminopeptidases from Escherichia coli and Pyrococcus furiosus. It has also been used in a study to examine the binding of a new class of pseudopeptide analog inhibitors.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Thermostable methionine aminopeptidase, which specifically liberates the N-terminal methioinine from proteins and peptides.
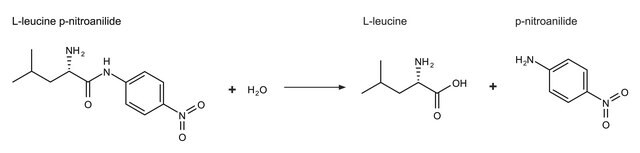
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1 μmol of Met from Met-Pro-Ala-Ala-Gly in 1 minute at pH 7.5 at 37 °C.
Physical form
Solution containing 0.01% Tween® 20, 0.1 mM CoCl2, and 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5.
Legal Information
TWEEN is a registered trademark of Croda International PLC
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
A Ben-Bassat et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 169(2), 751-757 (1987-02-01)
Methionine aminopeptidase (MAP) catalyzes the removal of amino-terminal methionine from proteins. The Escherichia coli map gene encoding this enzyme was cloned; it consists of 264 codons and encodes a monomeric enzyme of 29,333 daltons. In vitro analyses with purified enzyme
A new colorimetric assay for methionyl aminopeptidases: Examination of the binding of a new class of pseudopeptide analog inhibitors
Mitra, S., et al.
Analytical Biochemistry, 357, 7-7 (2006)
Sanghamitra Mitra et al.
Journal of biological inorganic chemistry : JBIC : a publication of the Society of Biological Inorganic Chemistry, 14(4), 573-585 (2009-02-10)
Methionine aminopeptidases (MetAPs) represent a unique class of protease that is capable of the hydrolytic removal of an N-terminal methionine residue from nascent polypeptide chains. MetAPs are physiologically important enzymes; hence, there is considerable interest in developing inhibitors that can
S Tsunasawa et al.
Journal of biochemistry, 122(4), 843-850 (1997-12-17)
A gene for a methionine aminopeptidase (MAP; EC 3.4.11.18), which catalyzes the removal of amino-terminal methionine from the growing peptide chain on the ribosome, has been cloned from the hyperthermophilic Archaeon, Pyrococcus furiosus, by a novel method effectively using its
R A Bradshaw et al.
Trends in biochemical sciences, 23(7), 263-267 (1998-08-11)
Removal of the initiator methionine and/or acetylation of the alpha-amino group are among the earliest possible chemical modifications that occur during protein synthesis in eukaryotes. These events are catalyzed by methionine aminopeptidase and N alpha-acetyltransferase, respectively. Recent advances in the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service