M9066
Microsomes from Liver, Pooled
from rat(Sprague-Dawley), male
Synonym(s):
Liver microsome preparation
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12161501
NACRES:
NA.47
Recommended Products
biological source
rat (Sprague-Dawley)
Quality Level
form
liquid
packaging
vial of ~10 mg
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Microsomes are the fraction of "submicroscopic” particles isolated from homogenates of liver and other tissues. Microsomes are rich in ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Application
Microsomes from Liver, Pooled has been used in following studies:
- inhibition of microsomal lipid peroxidation.
- hydroxylation of isorhynchophylline (ISOR) in rats.
Biochem/physiol Actions
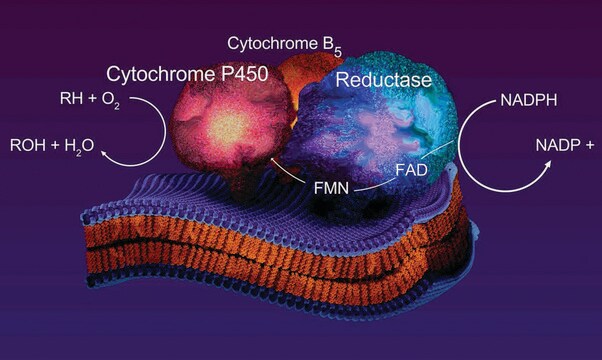
Liver microsomes are subcellular particles derived from the endoplasmic reticulum of hepatic cells. These microsomes are a rich source of drug metabolizing enzymes, including cytochrome P-450. Microsome pools from various sources are useful in the study of xenobiotic metabolism and drug interactions.
Microsomes might act as cell organelles and are actively involved in protein synthesis. Carbon monoxide-binding pigment of microsomes, named P-450, is an integral element of mixed function oxidase systems involved in the oxidative demethylation and hydroxylation of drugs and steroids. Murine liver microsomes plays a crucial role in degradation of small antimicrobial β2,2-amino acid derivatives.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Xiaofei Zhang et al.
ACS chemical neuroscience, 8(9), 1937-1948 (2017-06-02)
Metabotropic glutamate 2 receptors (mGlu
Metabolism of isorhynchophylline in rats detected by LC-MS.
Wang W
J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 13(1), 27-37 (2010)
Role of hemoprotein P-450 in fatty acid omega-hydroxylation in a soluble enzyme system from liver microsomes.
Lu AY and Coon MJ
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 243(6), 1331-1332 (1968)
Liver microsomes; an integrated morphological and biochemical study.
PALADE GE
The Journal of Biophysical and Biochemical Cytology, 2(2), 171-200 (1956)
Metabolism of small antimicrobial ?(2,2)-amino acid derivatives by murine liver microsomes.
Hansen T
Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet., 37(3), 191-201 (2012)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service