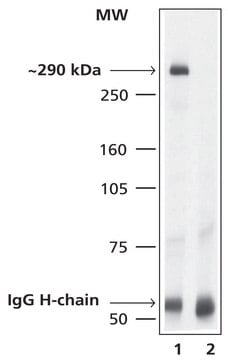
N1533
Nitric Oxide Synthase, Endothelial bovine
recombinant, expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
NOS III, ecNOS
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells
form
buffered aqueous solution
specific activity
≥0.3 units/mg protein
mol wt
135 (kDa/subunit, homodimer)
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
cow ... NOS3(287024)
Biochem/physiol Actions
For measuring NOS activity in the presence of exogenously added co-factors and/or inhibitors.
NOS is responsible for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine and is constituitively expressed in endothelial cells (eNOS) and brain (nNOS).
Responsible for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine; constituitively expressed in endothelial cells (eNOS) and brain (nNOS).
Suitable for measuring NOS activity in the presence of exogenously added co-factors and/or inhibitors.
Unit Definition
One unit of enzyme produces 1 nmole of nitric oxide per minute at 37 °C in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, containing 5 μM oxyhemoglobin, 1 mM CaCl2, 20 μg/ml calmodulin, 0.1 mM NADPH, 50 μM arginine, 12 μM tetrahydrobiopterin, and 170 μM DTT.
Physical form
Solution in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, with 10% glycerol, 5 mM CHAPS, and 100 μM DTT.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Inhibition of L-arginine metabolizing enzymes by L-arginine-derived advanced glycation end products.
Ying-Ling Lai et al.
Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition, 46(2), 177-185 (2010-03-11)
N(omega)-Carboxymethyl-arginine (CMA), N(omega)-carboxyethyl-arginine (CEA) and N(delta)-(5-hydro-5-methyl-4-imidazolon-2-yl)-ornithine (MG-H1) have been identified as L-arginine-derived advanced glycation end products (AGEs) formed by non-enzymatic reactions between reducing sugars such as glucose and amino groups in proteins. These AGEs are structurally analogous to endogenous inhibitors
Silviya R Stateva et al.
PloS one, 10(4), e0120798-e0120798 (2015-04-02)
Calmodulin (CaM) phosphorylated at different serine/threonine and tyrosine residues is known to exert differential regulatory effects on a variety of CaM-binding enzymes as compared to non-phosphorylated CaM. In this report we describe the preparation and characterization of a series of
Ying-Ling Lai et al.
Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition, 50(1), 84-89 (2012-01-17)
The cholesterol ozonolysis products secosterol-A and its aldolization product secosterol-B were recently detected in human atherosclerotic tissues and brain specimens, and have been postulated to play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and neurodegenerative diseases. We examined several oxidized
Heather S Bevan et al.
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology, 301(4), F733-F742 (2011-07-22)
Laminar shear stress is a key determinant of systemic vascular behavior, including through activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), but little is known of its role in the glomerulus. We confirmed eNOS expression by glomerular endothelial cells (GEnC) in
Yunzhou Dong et al.
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 13(9A), 2899-2910 (2008-07-16)
Oxidation and glycation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) promote vascular injury in diabetes; however, the mechanisms underlying this effect remain poorly defined. The present study was conducted to determine the effects of 'heavily oxidized' glycated LDL (HOG-LDL) on endothelial nitric oxide
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service