E7533
p3XFLAG-CMV™-7.1 Expression Vector
shuttle vector for transient expression of N-terminal 3xFLAG
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(2)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
tag
3X FLAG tagged
grade
Molecular Biology
form
buffered aqueous solution
quality
shuttle vector for transient expression of N-terminal 3xFLAG
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
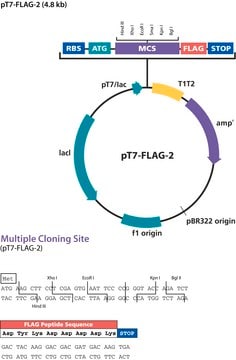
The p3XFLAG-CMV™-7.1 Expression Vector is a 4.7 kb derivative of pCMV5 used to establish transient intracellular expression of N-terminal 3XFLAG™fusion proteins in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) upstream of the multiple cloning region. This results in increased detection sensitivity using ANTI-FLAG M2 antibody. The third FLAG epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein.
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7.1 Expression Vector is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication is optimal when using an SV40 T antigenexpressing host.
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.2 kb derivative of pCMV5 used for transient intracellular expression of N-terminal 3XFLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) upstream of the multiple cloning region. The third FLAG epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein.
For more information, please see Vector Maps and Sequences
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7.1 Expression Vector is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication is optimal when using an SV40 T antigenexpressing host.
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.2 kb derivative of pCMV5 used for transient intracellular expression of N-terminal 3XFLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) upstream of the multiple cloning region. The third FLAG epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein.
For more information, please see Vector Maps and Sequences
Components
p3XFLAG-CMV™-7.1 Expression Vector 20 μg (E4026) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
p3XFLAG-CMV™-7-BAP Control Plasmid 20 μg (C7472) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
p3XFLAG-CMV™-7-BAP Control Plasmid 20 μg (C7472) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
Principle
The promoter-regulatory region of the human cytomegalovirus drives transcription of FLAG®-fusion constructs.
Legal Information
This product is covered by the following patents owned by Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC: US6,379,903, US7,094,548, JP4405125,EP1220933, CA2386471 and AU774216.
3xFLAG is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
p3xFLAG-CMV is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Yongwei Zhang et al.
Nucleic acids research, 40(8), e55-e55 (2012-01-14)
We describe a novel cloning method termed SLiCE (Seamless Ligation Cloning Extract) that utilizes easy to generate bacterial cell extracts to assemble multiple DNA fragments into recombinant DNA molecules in a single in vitro recombination reaction. SLiCE overcomes the sequence
Xufang Deng et al.
Virology journal, 7, 348-348 (2010-11-30)
Marek's disease virus (MDV) is an oncogenic herpesvirus, which causes malignant lymphoma in chickens. The Meq protein of MDV, which is expressed abundantly in MDV-infected cells and in Marek's disease (MD) tumor cells, functions as a transcriptional activator and has
Fbxo45 forms a novel ubiquitin ligase complex and is required for neuronal development.
Saiga, T., et al.
Molecular Biology of the Cell, 29, 3529-3529 (2009)
Xiaodu Wang et al.
Sheng wu gong cheng xue bao = Chinese journal of biotechnology, 26(1), 16-21 (2010-04-01)
M2 protein of influenza A virus is encoded by a spliced mRNA derived from RNA segment 7 and plays an important role in influenza virus replication. It is also a target molecule of anti-virus drugs. We extracted the viral genome
Elizabeth R Moore et al.
Microbiology (Reading, England), 157(Pt 3), 830-838 (2010-11-27)
Chlamydia trachomatis is an obligate intracellular pathogen that replicates within a parasitophorous vacuole termed an inclusion. The chlamydial inclusion is isolated from the endocytic pathway but fusogenic with Golgi-derived exocytic vesicles containing sphingomyelin and cholesterol. Sphingolipids are incorporated into the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service