M8131
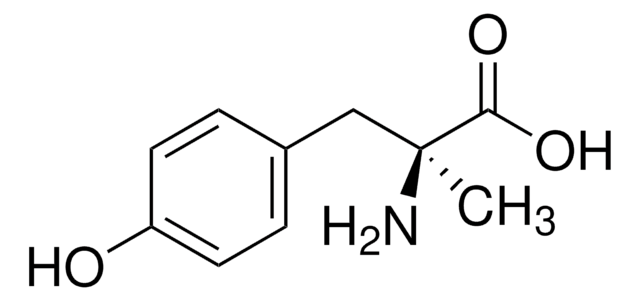
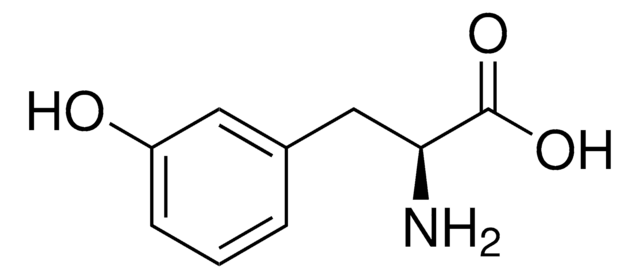
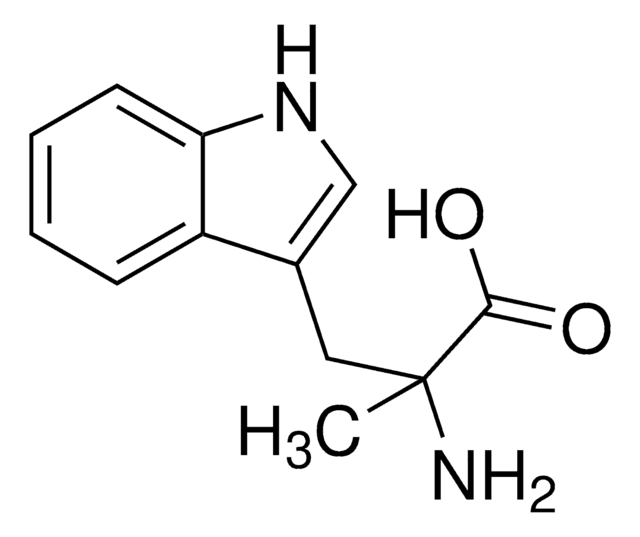
α-Methyl-L-tyrosine
≥98% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
L-2-Methyl-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)alanine, L-AMPT
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(5)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C10H13NO3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
195.22
Beilstein:
2368400
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
Assay
≥98% (TLC)
form
powder
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
C[C@](N)(Cc1ccc(O)cc1)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H13NO3/c1-10(11,9(13)14)6-7-2-4-8(12)5-3-7/h2-5,12H,6,11H2,1H3,(H,13,14)/t10-/m0/s1
InChI key
NHTGHBARYWONDQ-JTQLQIEISA-N
Gene Information
human ... TH(7054)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
α-Methyl-L-tyrosine has been used as an inhibitor tyrosine hydroxylase:
- to test its effect during acute stress in zebrafish
- in cannabinoid receptor type-1 (CB1) knockout and wild type mice, to test its effect on norepinephrine turnover
- to test catecholamines depletion on stress in rat spleen samples
- to block dopamine synthesis in dopaminergic neurons
α-Methyl-L-tyrosine is used to determine whether Fe2/ methamphetamine (METH) -induced cell death is dependent on cytosolic dopamine and iron mediated oxidative stress.
Biochem/physiol Actions
α-Methyl-L-tyrosine (L-AMPT) acts as a competitive inhibitor of tyrosine hydroxylase and inhibits the conversion of tyrosine to L-DOPA and eventually lowers dopamine synthesis in cytosol. AMPT at low concentrations can be used as a potent therapeutic for refractory dystonia or dyskinesia. It also helps in decreasing catecholamine concentration in pheochromocytoma patients.
Tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor.
Other Notes
Active isomer
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Progressive degeneration of human mesencephalic neuron-derived cells triggered by dopamine-dependent oxidative stress is dependent on the mixed-lineage kinase pathway.
Lotharius J
The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(27), 6329-6342 (2005)
Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Deletion from Catecholaminergic Neurons Protects from Diet-Induced Obesity.
Raj Kamal Srivastava et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 23(20) (2022-10-28)
High-calorie diets and chronic stress are major contributors to the development of obesity and metabolic disorders. These two risk factors regulate the activity of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). The present study showed a key role of the cannabinoid type
Renan Idalencio et al.
General and comparative endocrinology, 252, 236-238 (2017-07-19)
In this article, we show that the tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor α-Methyl-l-tyrosine (AMPT) decreased the responsiveness of the zebrafish stress axis to an acute stressful challenge. These effects were specific for responses to stimulation, since unstimulated (basal) cortisol levels were not
Sergio Ortiz-Padilla et al.
Neuropharmacology, 166, 107920-107920 (2019-12-25)
Dopaminergic neurons have the ability to release Dopamine from their axons as well as from their soma and dendrites. This somatodendritically-released Dopamine induces an autoinhibition of Dopaminergic neurons mediated by D2 autoreceptors, and the stimulation of neighbor GABAergic neurons mediated
Low dose alpha-methyl-para-tyrosine (AMPT) in the treatment of dystonia and dyskinesia.
Ankenman R and Salvatore MF
The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 19(1), 65-69 (2007)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service