MAK320
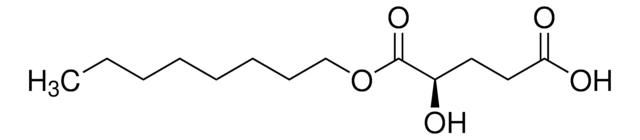
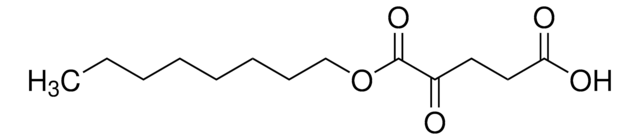
D-2-Hydroxyglutarate (D2HG) Assay Kit
sufficient for 200 fluorometric reactions
Synonym(s):
D2HG Test Kit
About This Item
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 200 reactions (Fluorometric)
detection method
fluorometric
relevant disease(s)
cancer; neurological disorders
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
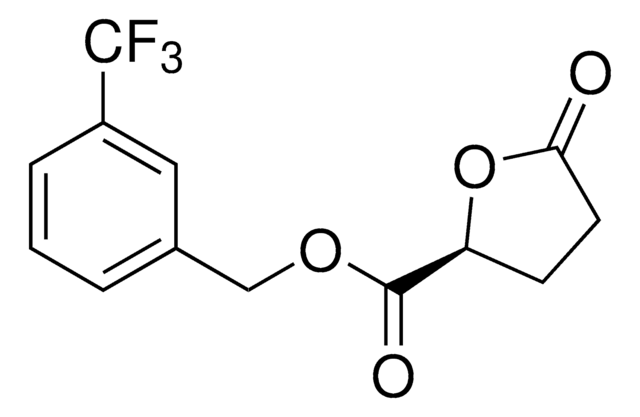
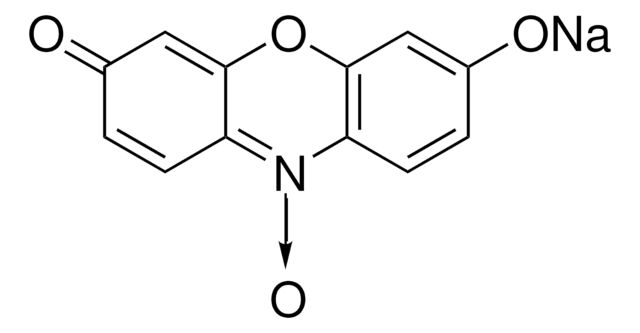
General description
Features and Benefits
- Highly sensitive and rapid enzymatic assay for the detection of D2HG levels in various biological fluids
- Supportive calculator (Click here to download a calculator excel file) Analyze results based on your experimental data!
- Quick instruction bench card - to assure your experimental success
- More experiments in one kit - contains sufficient reagents for 200 tests
- Detection time: only 30-60 minutes
Suitability
Principle
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
Regulatory Listings
Regulatory Listings are mainly provided for chemical products. Only limited information can be provided here for non-chemical products. No entry means none of the components are listed. It is the user’s obligation to ensure the safe and legal use of the product.
PDSCL
Please refer to KIT Component information
PRTR
Please refer to KIT Component information
FSL
Please refer to KIT Component information
ISHL Indicated Name
Please refer to KIT Component information
ISHL Notified Names
Please refer to KIT Component information
Cartagena Act
Please refer to KIT Component information
JAN Code
キットコンポーネントの情報を参照してください
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service