CS0980
Chitinase Assay Kit
sufficient for 100 multiwell tests
Synonym(s):
Chitinase Activity Detection Kit
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12161503
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 100 multiwell tests
Quality Level
absorbance ratio
405 nm (Absorbance)
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
human ... CHIA(27159) , CHIT1(1118)
General description
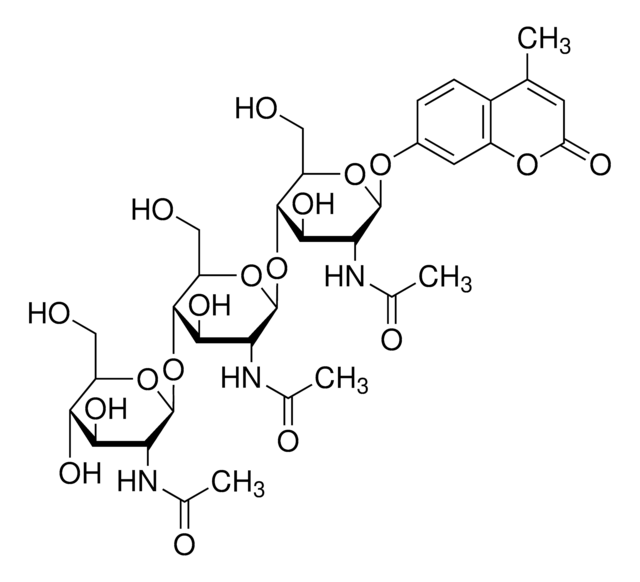
The Chitinase Assay Kit is based on the enzymatic hydrolysis of chitinase substrates. The hydrolysis releases p-nitrophenol, which can be measured colormetrically at 405 nm.
Application
Chitinase Assay Kit has been used in screening chitinase activity of recombinant chitinase from yeast, Metschnikowia fructicola, bacterial endophyte 3A12 and Clostridium difficile spores.
The kit provides all the reagents required for efficient detection of chitinase activity in fungal and bacterial growth media, macrophage lysates, and purified enzyme preparations. In addition, the kit provides three different substrates for the detection of the various types of the chitinolytic activity:
The kit provides all the reagents required for efficient detection of chitinase activity in fungal and bacterial growth media, macrophage lysates, and purified enzyme preparations. In addition, the kit provides three different substrates for the detection of the various types of the chitinolytic activity:
- 4-Nitrophenyl N,N′-diacetyl-β-D-chitobioside - substrate suitable for exochitinase activity detection (chitobiosidase activity)
- 4-Nitrophenyl N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide - substrate suitable for exochitinase activity detection (β-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Chitinase catalyzes the hydrolytic cleavage of the β-1→4-glycoside bond present in biopolymers of N-acetylglucosamine, primarily in chitin. Chitinases are widely distributed in living organisms and are found in fungi, bacteria, parasites, plants, and animals. They are classified in families based on amino acid sequence similarities.
The chitinolytic enzymes are also categorized based on their enzymatic action on chitin substrates. Endochitinases are defined as the enzymes catalyzing the random cleavage at internal points in the chitin chain. Exochitinases catalyze the progressive release of acetylchitobiose or N-acetylglucosamine from the non-reducing end of chitin, and are referred to as chitobiosidase and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, respectively.
Chitinases perform different functions in different organisms. In bacteria, they are mainly involved in nutritional processes. In yeast and various fungi, these enzymes participate in morphogenesis. In animals and plants, chitinases primarily play a role in the defense of the organism against pathogen attack.
The chitinolytic enzymes are also categorized based on their enzymatic action on chitin substrates. Endochitinases are defined as the enzymes catalyzing the random cleavage at internal points in the chitin chain. Exochitinases catalyze the progressive release of acetylchitobiose or N-acetylglucosamine from the non-reducing end of chitin, and are referred to as chitobiosidase and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, respectively.
Chitinases perform different functions in different organisms. In bacteria, they are mainly involved in nutritional processes. In yeast and various fungi, these enzymes participate in morphogenesis. In animals and plants, chitinases primarily play a role in the defense of the organism against pathogen attack.
Analysis Note
The kit assay is based on the enzymatic hydrolysis of chitinase substrates. This hydrolysis releases p-nitrophenol (4-nitrophenol), which upon ionization in basic pH can be measured colorimetrically at 405 nm.
Kit Components Only
Product No.
Description
- Assay Buffer 20 mL
- 4-Nitrophenyl N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide 10 mg
- 4-Nitrophenyl N,N′-diacetyl-β-D-chitobioside 5 mg
- 4-Nitrophenyl β-D-N,N′N′′-triacetylchitotriose 1 mg
- Chitinase from Trichoderma viride 1 mg
- p-Nitrophenol Solution, 10 mM 1 mL
- Sodium Carbonate 1 g
related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Target Organs
Liver,Kidney
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Ahmed Akrem et al.
Acta crystallographica. Section F, Structural biology and crystallization communications, 67(Pt 3), 340-343 (2011-03-12)
A chitinase has been isolated and purified from Crocus vernus corms. N-terminal amino-acid sequence analysis of the approximately 30 kDa protein showed 33% identity to narbonin, a seed protein from Vicia narbonensis L. The C. vernus chitinase was crystallized by the
E Patrick Fuerst et al.
Frontiers in plant science, 8, 2259-2259 (2018-02-08)
Seeds have well-established passive physical and chemical defense mechanisms that protect their food reserves from decay-inducing organisms and herbivores. However, there are few studies evaluating potential biochemical defenses of dormant seeds against pathogens. Caryopsis decay by the pathogenic Fusarium avenaceum
Functional characterization of Clostridium difficile spore coat proteins
Permpoonpattana P, et al.
Journal of Bacteriology, 195, 1492?1503-1492?1503 (2013)
The main virulence determinant of Yersinia entomophaga MH96 is a broad host range insect active, Toxin Complex
Hurst,M et al.
Journal of Bacteriology (2011)
Patima Permpoonpattana et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 193(23), 6461-6470 (2011-09-29)
Clostridium difficile is an important human pathogen and one where the primary cause of disease is due to the transmission of spores. We have investigated the proteins found in the outer coat layers of C. difficile spores of pathogenic strain
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service