G7163
α-Galactosidase, positionally specific from Escherichia coli
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
1,6-alpha-D-galactoside galactohydrolase, alpha-Galactosidase, melibiase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Quality Level
form
buffered aqueous solution
specific activity
≥20 units/mg protein
mol wt
80 kDa
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
Escherichia coli CFT073 ... melA(1037886)
Related Categories
Biochem/physiol Actions
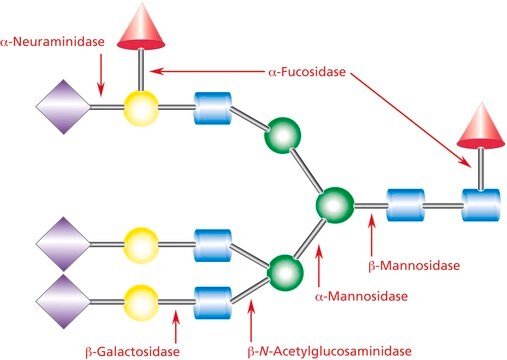
Cleaves α(1→3)- and α(1→6)-linked, non-reducing terminal galactose from complex carbohydrates and glycoproteins. It is particularly efficient for removing α-linked galactose under conditions where the pH must be neutral or above, for example, with live cells.
Unit Definition
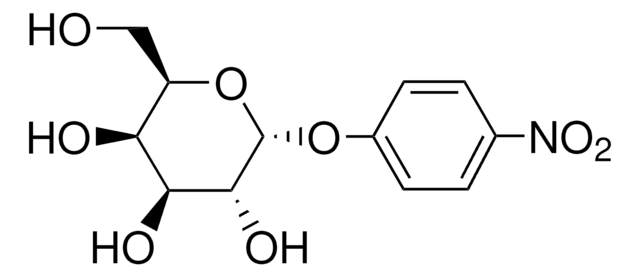
One unit will hydrolyze 1 μmole of p-nitrophenyl α-D-galactopyranoside per min at pH 6.5 at 25 °C.
Physical form
This product is a sterile-filtered aqueous buffered solution.
inhibitor
Product No.
Description
Pricing
substrate
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
K Schmid et al.
European journal of biochemistry, 67(1), 95-104 (1976-08-01)
The utilization by Escherichia coli K12 of raffinose as sole carbon source depends on a new raffinose transport system, an invertase and an alpha-galactosidase specified by the Raf-plasmid D1021. The alpha-galactosidase was purified to homogeneity from a mutant strain with
Shuo Gao et al.
Frontiers in chemistry, 9, 709581-709581 (2021-08-03)
For wide applications of the lacZ gene in cellular/molecular biology, small animal investigations, and clinical assessments, the improvement of noninvasive imaging approaches to precisely assay gene expression has garnered much attention. In this study, we investigate a novel molecular platform
Costanza Simoncini et al.
The neurologist, 18(6), 413-414 (2012-11-02)
Fabry disease (FD) is a rare, X-linked lysosomal storage disorder with multiorgan involvement. FD is caused by a partial or total deficit of α-galactosidase A enzyme, which is responsible for the accumulation of glycosphingolipids in a variety of cell types.
Masahisa Kobayashi et al.
Molecular genetics and metabolism, 107(4), 711-715 (2012-11-14)
Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal disorder resulting from mutations in the α-galactosidase A (GLA) gene. Recent reports described that the E66Q mutation of GLA is not a disease-causing mutation. However, no pathological study was reported. We carried out pathological
Dominique P Germain et al.
Orphanet journal of rare diseases, 7, 91-91 (2012-11-28)
Fabry disease (FD) is a genetic disorder resulting from deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme α-galactosidase A (α-Gal A), which leads to globotriaosylceramide (GL-3) accumulation in multiple tissues. We report on the safety and pharmacodynamics of migalastat hydrochloride, an investigational pharmacological
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service